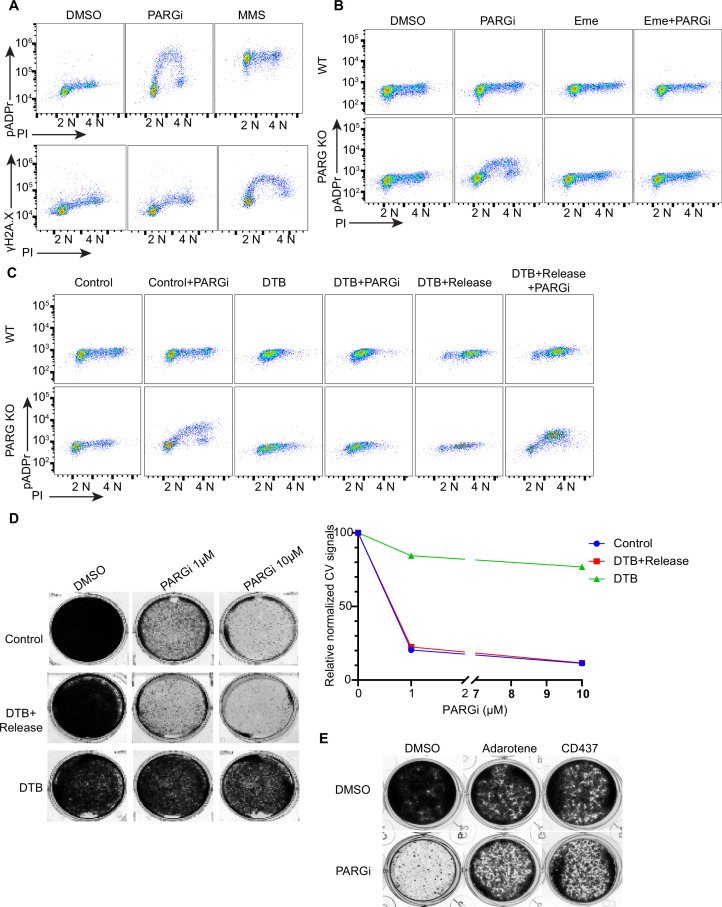
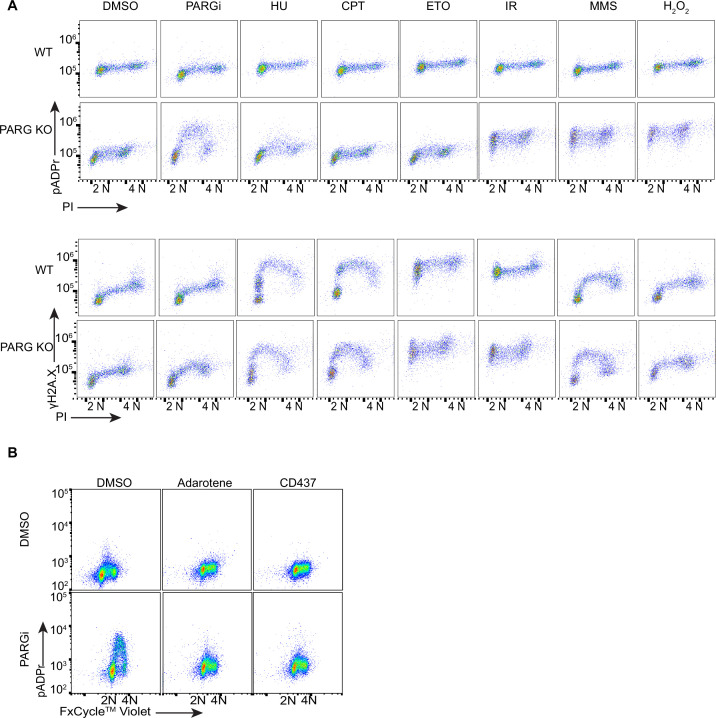
Figure 3. PARGi treatment induces S-phase-specific pADPr signaling in PARG KO cells.
(a) HEK293A WT and PARG KO cells were treated with DMSO or 10 µM PARGi for 4 hr or 0.01% MMS for 30 min and then fixed and stained with anti-pADPr antibody or anti-γH2A.X antibody and PI. (b) HEK293A WT and HEK293A PARG KO cells were mock-treated or pre-treated with 2 µM emetine for 90 min and then treated with PARGi for an additional 4 hr. Cells were fixed and stained with anti-pADPr antibody and PI. (c) HEK293A PARG KO cells were synchronized with double thymidine block (DTB). Cells remained with DTB or were released from DTB, treated with 10 µM PARGi for 4 hr, and then fixed and stained with anti-pADPr antibody and PI. (d) Representative images and results (left) of clonogenic assays conducted using control cells and DTB synchronized or released HEK293A PARG KO cells treated with the indicated doses of PARGi for 7 days, and quantification of crystal violet staining assay (right). (e) Results of clonogenic assays were conducted in PARG KO cells with indicated treatment for 7 days (PARGi, 1 µM; adarotene, 200 nM; CD437, 800 nM).