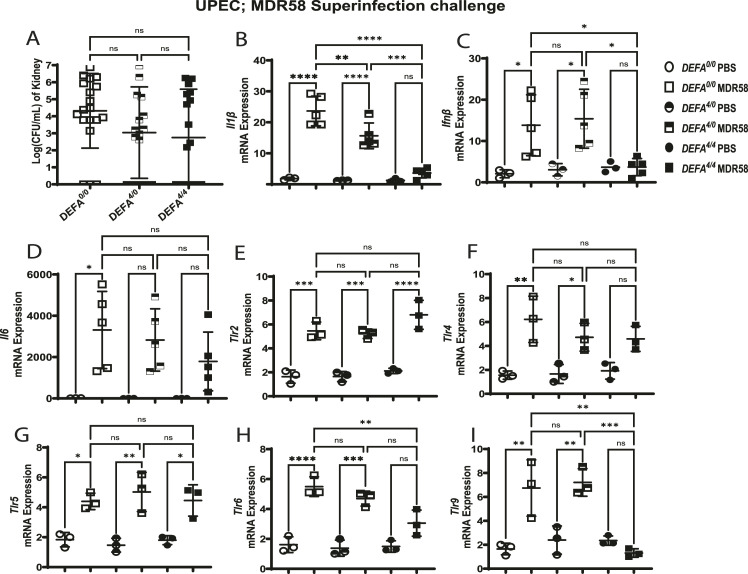
Figure 6. Human transgenic DEFA1A3 DNA copies modulate kidney pro-inflammatory responses in a bacterial viability–independent manner.
(A) Individual kidneys from DEFA0/0, DEFA4/0, and DEFA4/4 mice were quantified for CFU/ml after superinfection challenges with pyelonephritis multi-drug–resistant strain; MDR58 or vehicle. RT–qPCR from infected mouse kidneys was applied to assess induction of Toll-like superfamily and pro-inflammatory downstream gene targets. (B) Down-regulation of kidney IL1β mRNA gene expression follows a gene dose–dependent pattern in infected kidneys. (C) On the contrary, only DEFA4/4 mice displayed lower IFNβ mRNA expression levels compared with infected kidneys from littermates with 0 and 4 DEFA1A3 copies. (D) IL6 gene expression was non-significantly lower in infected DEFA4/4 kidneys. (E, F, G, H) Toll-like receptor targets quantified for mRNA expression were compared between infected kidneys from mouse different DEFA1A3 copy numbers with no differences observed for (E) Tlr2, (F) Tlr4, and (G) Tlr5. (H) Tlr6 kidney mRNA expression differences were significantly lower only for infected DEFA4/4 mice compared with littermates. (I) Tlr9 kidney mRNA induction down-regulated for infected DEFA4/4 mice compared with infected littermates. No differences were recorded in vehicle-challenged mice. Data are represented as the mean CFU/ml or mRNA expression ± SD of saline or pyelonephritis multi-drug–resistant strain–challenged kidneys at 6 hpi. Differences were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test for groups of mice ranging from 3 to 10 biological replicates.