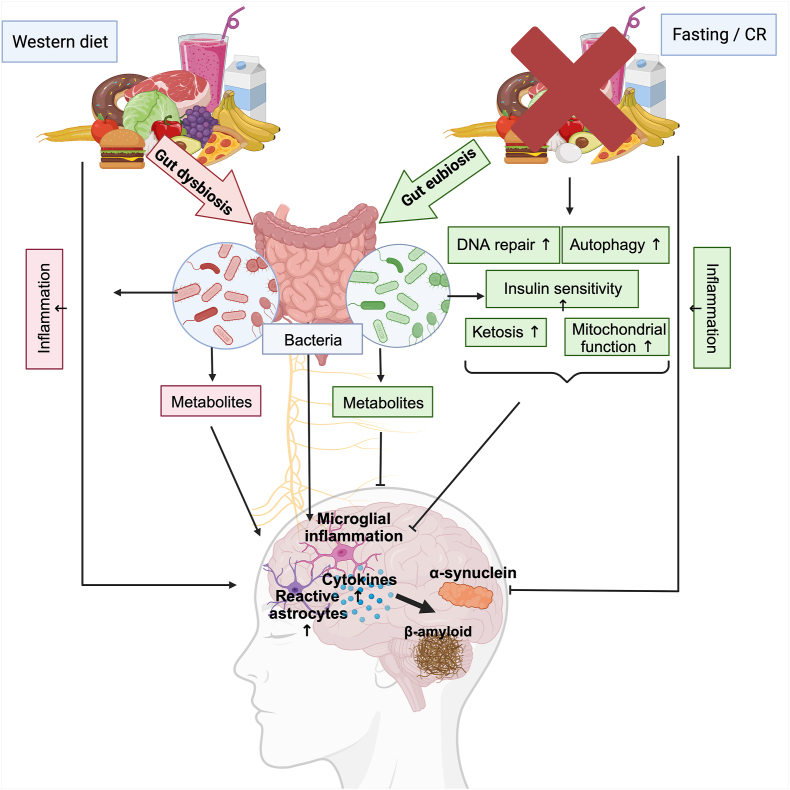
FIGURE 1.
Underlying mechanisms. This figure illustrates the possible underlying mechanisms of the beneficial impact of fasting and CR on ND. While a typical western diet usually leads to gut dysbiosis and an increase in inflammation, the abstinence or reduction of food can have a positive impact on cognitive function by changing the gut microbiota composition and its metabolite secretion [41,42,46]. Several additional mechanisms including DNA repair, increased autophagy, upregulated mitochondrial function, increased insulin sensitivity, increased ketone body production, and decreased overall inflammation may result in beneficial impacts on cognitive function [[73], [74], [75]]. Abbreviations: CR, calorie restriction; ND, neurodegenerative disease. This image was generated using BioRender software (www.biorender.com).