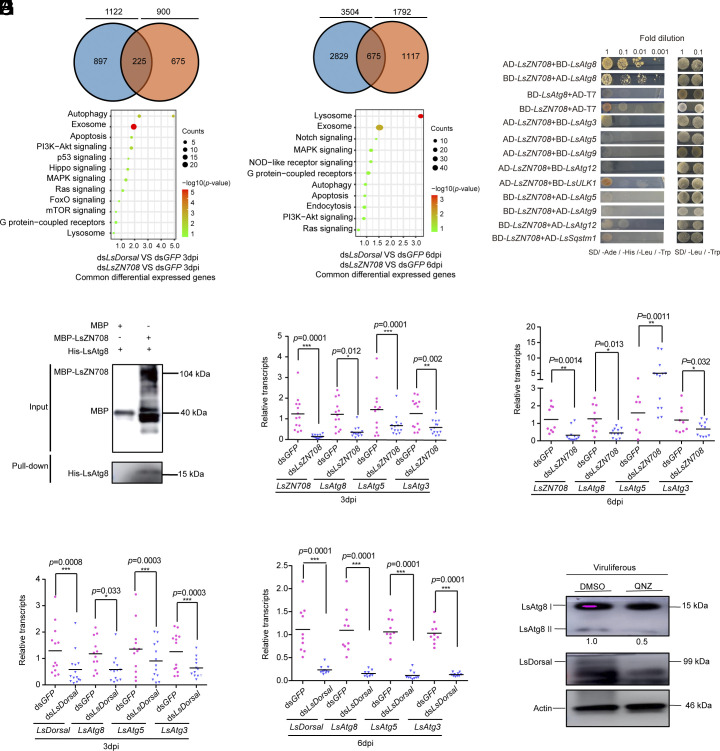
Fig. 4.
Downstream immune-related effectors of toll pathway that potentially involved in the antiviral response of L. striatellus against RSV infection. (A and B) KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of the common DEG in nonviruliferous L. striatellus treated with a dsLsDorsal or dsLsZN708 and RSV crude extracts at 3 dpi (A) and 6 dpi (B). Significant differences were indicated when log2 (fold change) ratio was ≥1 and P ≤ 0.05. (C) The interaction between LsZN708 and autophagy protein LsAtg8 through Y2H assay. The different combinations of constructs transformed into yeast cells were grown on selective medium SD/-Leu/-Trp, and interactions were detected on SD/-Ade/-His/-Leu/-Trp. The images were taken after 3 d of incubation at 30 °C. (D) The interaction between LsZN708 and LsAtg8 protein through an in vitro pull-down assay. MBP-ZN708 fusion protein was used to pull-down with His-Atg8. MBP was used as negative control and His-Atg8 was further detected with anti-His antibody. (E–H) Effects of LsZN708 or LsDorsal knockdown on the transcription levels of autophagy-related genes (LsAtg8, LsAtg5 and LsAtg3) in nonviruliferous L. striatellus treated with dsLsZN708 (E and F) or dsLsDorsal (G and H) and RSV crude extracts at 3 or 6 dpi. (I) Protein level of LsAtg8II in viruliferous L. striatellus treated with QNZ inhibitor for 48 h (DMSO was used as control). Three biological replicates were performed for each experiment. Significance analysis was performed using the t test method. * represents a significant difference (P < 0.05), ** and *** represent extremely significant differences (P < 0.01 and P < 0.001). The error bars represent the SE of the mean.