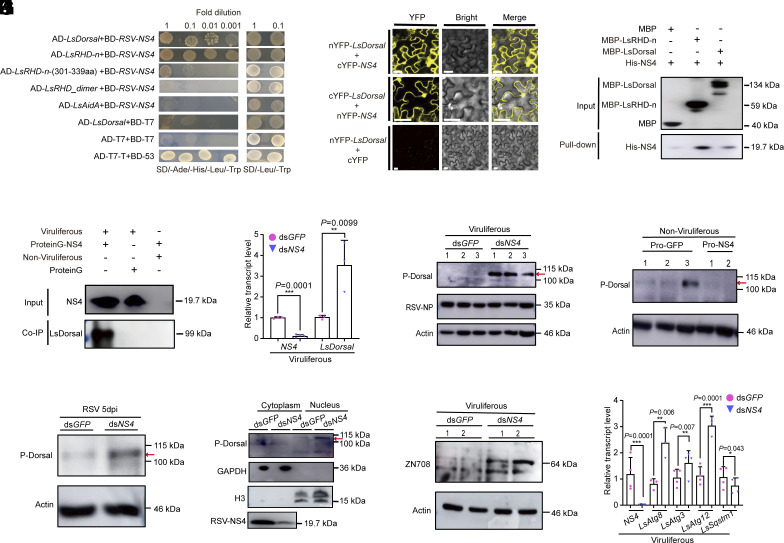
Fig. 5.
Nonstructural protein NS4 of RSV (RSV NS4) participates in the viral counterdefense strategy through the inhibition of LsDorsal phosphorylation. (A) Interaction of RSV NS4 with LsDorsal or RHD-n domain (301 to 339 aa) of LsDorsal was confirmed by Y2H assay. (B) BIFC assays verified the interaction between LsDorsal and NS4 in the cell nucleus and cytoplasm of Nicotiana benthamiana leaves. (C) The interaction between LsDorsal and NS4 was confirmed by an in vitro pull-down assay. MBP-Dorsal and MBP-RHD-n proteins were used to pull-down with His-NS4. His-NS4 was further detected with anti-His antibody. (D) The Co-IP assay confirmed the interaction between LsDorsal and NS4 of L. striatellus in vivo. The crude extracts of L. striatellus were prepared and immunoprecipitated by ProteinG-NS4 combinations. The coimmunoprecipitated proteins were detected with LsDorsal antibody. (E and F) Effect of NS4 knockdown on the transcription (E) and phosphorylation (F) levels of LsDorsal in viruliferous L. striatellus (dsGFP as control). (G) Phosphorylation level of LsDorsal in nonviruliferous L. striatellus treated with purified NS4 protein (GFP protein as control). (H) Phosphorylation level of LsDorsal in nonviruliferous L. striatellus treated with dsNS4 and RSV crude extracts at 5 dpi. (I–K) Effect of NS4 knockdown on the protein level of p-Dorsal in the nucleus and cytoplasm (I), the protein level of LsZN708 (J), and relative transcription levels of autophagy genes LsAtg8, LsAtg3, LsAtg12 and LsSqstm1 (K) in viruliferous L. striatellus. Three biological replicates were performed for each experiment. The t test method was used for significance analysis. * represents significant difference (P < 0.05), * and *** represent extremely significant difference (P < 0.01 and P < 0.001), n.s. means no significance. The error bars represent the SE of the mean.