Figure 1. RNA modifications dependent on redox coenzymes.
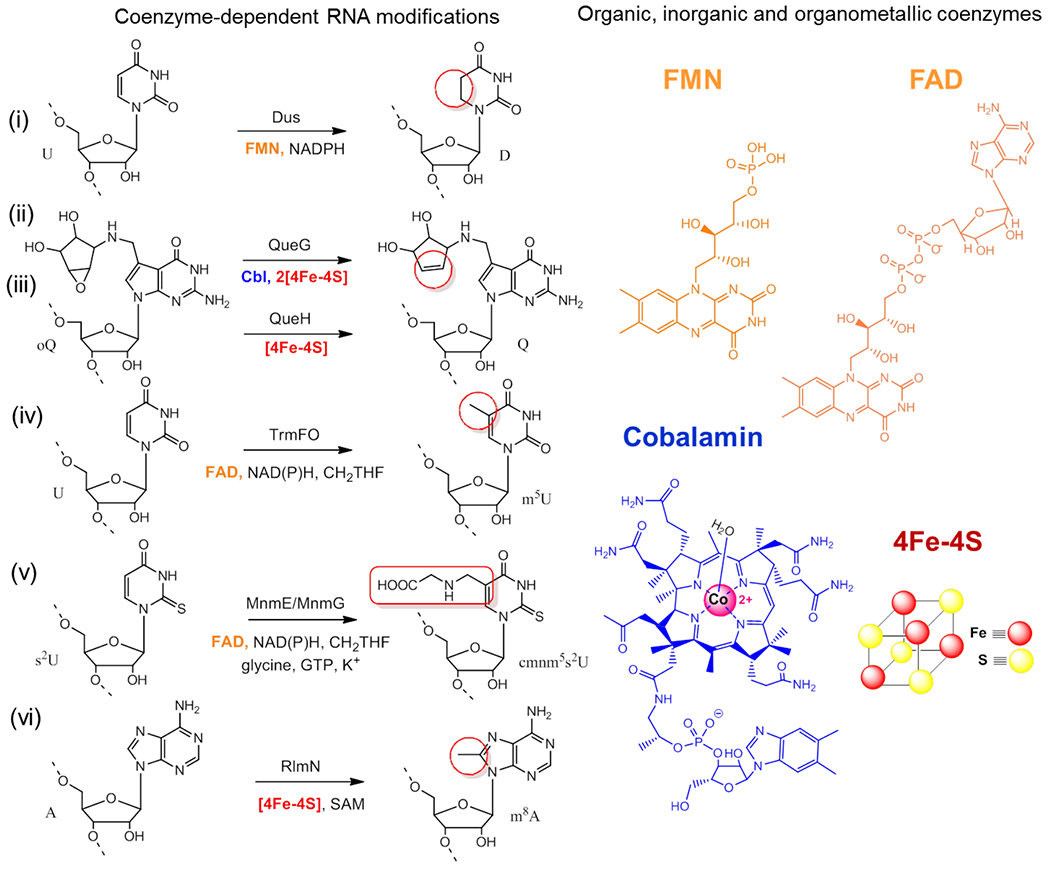
Left side : biosynthetic RNA modifications for: (i) the reduction of uridine to dihydrouridine (D) catalyzed by the dihydrouridine synthases (Dus), (ii) the oQ reduction to Q by QueG and QueH, (iii) the reductive methylation of uridine into m5U by TrmFO, (iv) the carboxymethylaminomethylation of uridine into cmnm5U catalyzed by MnmE/mnmG complex (v) the methylation of adenine to m8A by RlmN. (vi) The chemical groups of each modification are boxed in red and the respective enzyme(s) that catalyze each reaction are indicated. Right side: Biochemical coenzymes used for RNA modifications: flavins (FMN and FAD) in orange, cobalamin (CbI) in blue and its metal in magenta, while the cubic 4Fe-4S cluster is represented with Fe atoms in red and sulfur in yellow.
