Figure 5. Formaldehyde shunt to activate an apoprotein of a folate and flavin-dependent methyltransferase.
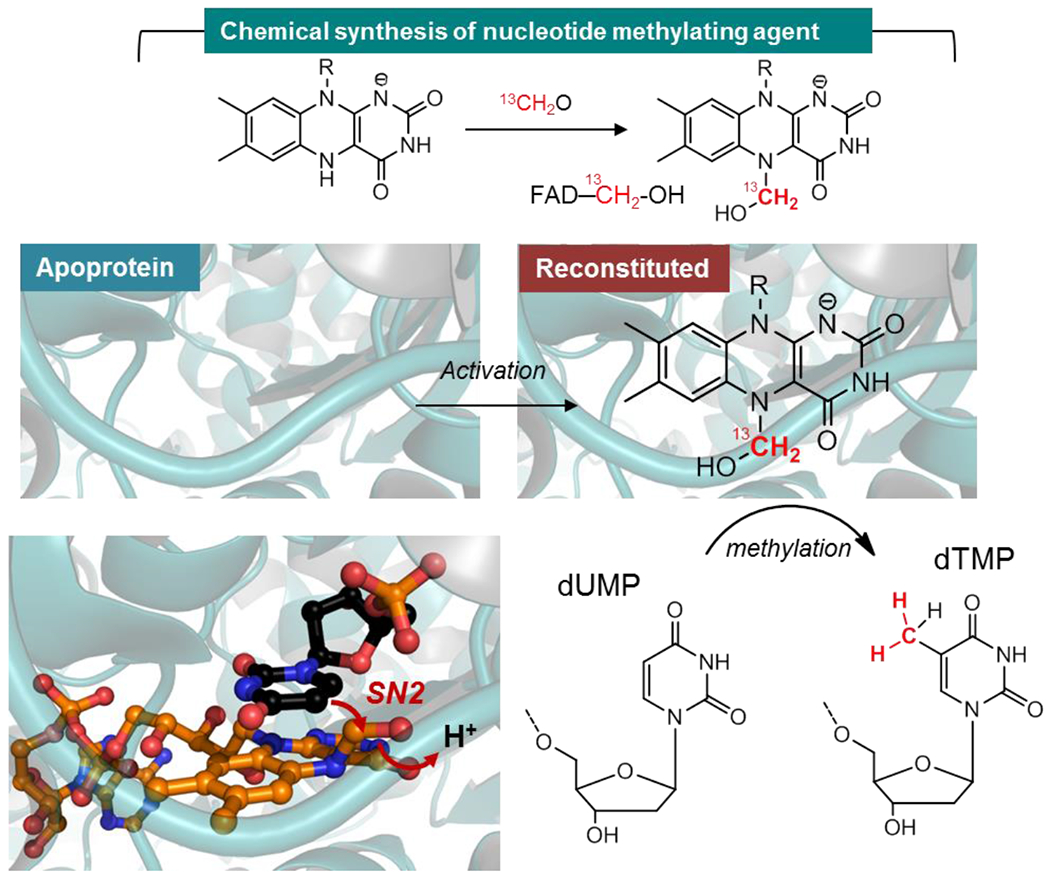
FADH− (reduced flavin), obtained by the reduction of oxidized FAD with dithionite, activates 13C-labeled formaldehyde via the N5 of the isoalloxazine to give an air-labile flavin carbinolamine. The latter can be reconstituted in an apoprotein version of Thermus thermophilus thymidylate synthase (ThyX) that uses flavin and folate to catalyze the reductive methylation of the uracil C5 of dUMP to dTMP. This reaction is similar to that of TrmFO or RlmFO. Once reconstituted with the synthetic carbinolamine under anaerobic conditions, the methyltransferase is active and can readily methylate dUMP. The crystallographic structure of this carbinolamine intermediate (orange) is shown in complex with dUMP (black) by structural alignment. Once activated, the C5 uracil of the substrate attacks the electrophilic methylene of the carbinolamine allowing its transfer from the flavin to dUMP.
