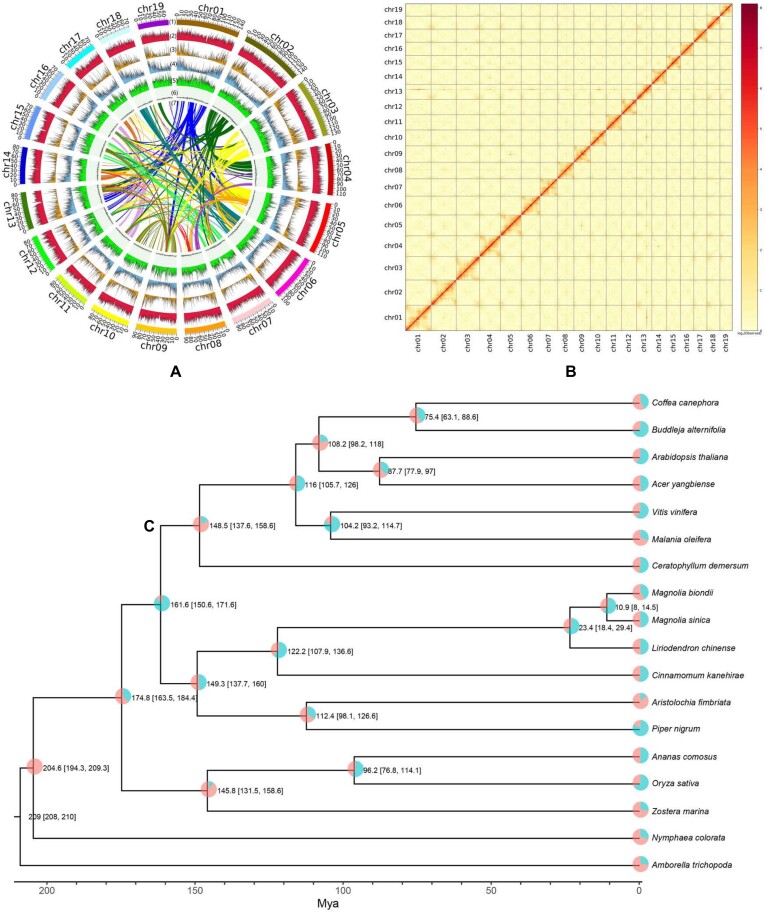
Figure 2:
Genomic character and genome evolution of Magnolia sinica. (A) The genome features across 19 chromosomes of M. sinica. (1) Nineteen pseudochromosomes. (2) Class I transposable element (TE) density (including long terminal repeats [LTRs], long and short interspersed nuclear elements). (3) Class II TE (DNA and Heliron) density. (4) Coding gene (messenger RNA) density. (5) The density of single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) loci. (6) GC content. (7) collinear blocks. (B) Hi-C interaction heatmap for the M. sinica genome showing interactions among 19 chromosomes. (C) The phylogenetic tree of 18 species showing the proportions of the gene families that contracted and expanded (pink: contracted; blue-green: expanded; values at the nodes represent the time of differentiation and 95% CI).