Fig. 1. S. epidermidis PSMs and construction of isogenic psm deletion mutants.
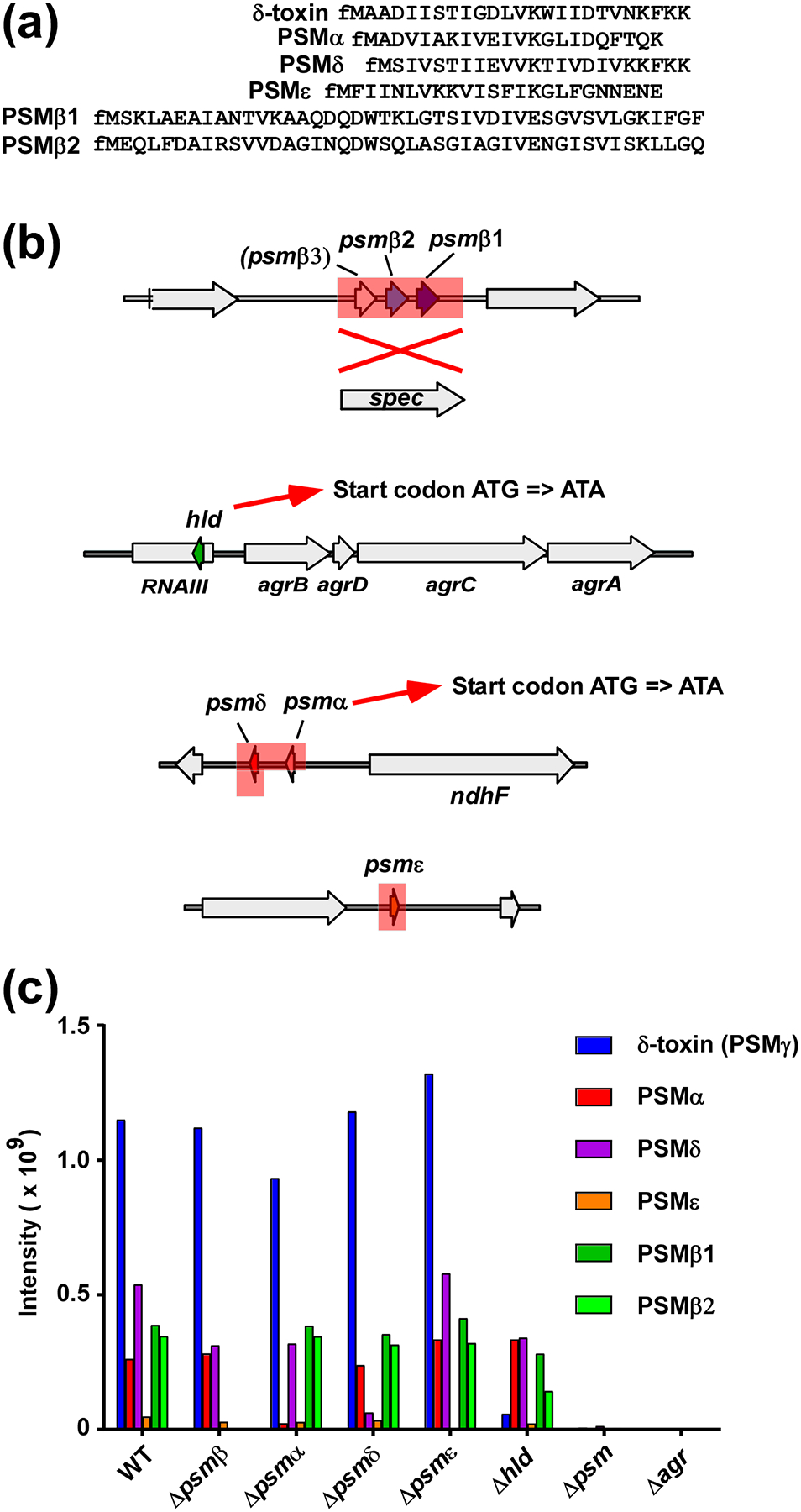
(a) Amino acid sequences of S. epidermidis PSMs. Note all PSMs have an N-terminal formylated methionine (fM) due to export by a dedicated ABC transporter without a signal peptide [55]. (b) S. epidermidis psm deletion mutants. The psmβ deletion mutant was constructed by replacement of the entire psmβ operon with a spectinomycin resistance cassette. Note the hypothetical PSMβ3 peptide does not appear to be produced. The quintuple (total) psm deletion mutants was then constructed by sequential deletion of the other psm loci, in the order as shown from top to bottom. Single psm deletion mutants were also constructed. In the case of hld (encoding δ-toxin) and psmα, start codon mutations were introduced instead of complete gene deletions, so as not to interfere with production of RNAIII or expression of psmδ, respectively. Deleted or replaced sections are shadowed in red. (c) Analysis of PSM production pattern by RP-HPLC/MS of all psm mutants used in thus study.
