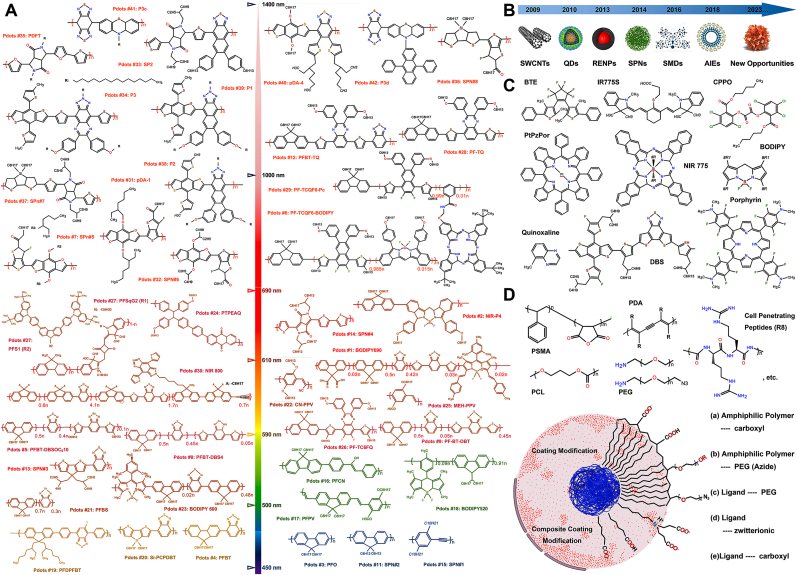
Fig. 4.
Molecular Design Strategies and Surface Modification. A). Chemical structures of the published Pdots. The chemical structural formula's color represents the emission peak's spectral position. Rx represents the side chain chemical structural formula. Drawing inspiration and reprinted with permission from Ref. [65]. Copyright 2021 American Chemical Society. B). Hotspot optical nanomaterials at different time nodes. Abbreviations: SWCNTs, single-walled carbon nanotubes; QDs, quantum dots; RENPs, rare-earth-doped nanoprobes; SPNs, supramolecular polymer networks; SMDs, small-molecule dyes; AIEs, aggregation-induced emission luminogens. Drawing inspiration and reprinted with permission from Ref. [92]. Copyright 2020 American Chemical Society. C). The common doped and combined fluorescent dyes (donor-acceptor or donor-bridge-acceptor) inside or outside the π-conjugated chain. Abbreviations: BTE, (1,2-bis(2,4-dimethyl-5-phenyl-3-thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluoro-1-cyclopentene; CPPO, Bis{3,4,6-trichloro-2-[(pentyloxy)carbonyl]phenyl} oxalate; BODIPY, 10-(4-(2,5-dioxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrol-1-yl)phenyl)-5,5; DBS, dithienyl-benzo selenadiazole; PtBzPor, (meso-tetraphenyl tetrabenzoporphyrin platinum (II), etc. D). Common amphiphilic polymers or compounds used for surface chemical modification. Drawing inspiration and reprinted with permission from Ref. [2]. Copyright 2020 American Chemical Society. Abbreviations: PSMA, poly (styrene-co-maleic anhydride); PDA, polydiacetylene; PEG, polyethylene glycol; PCL, Poly (ε-caprolactone), etc. Exposed chemical groups that can be used for functionalization after modification, which could form a single or multiple layer surface modification coating. Or include processes such as electrostatic bonding and self-forming coating.