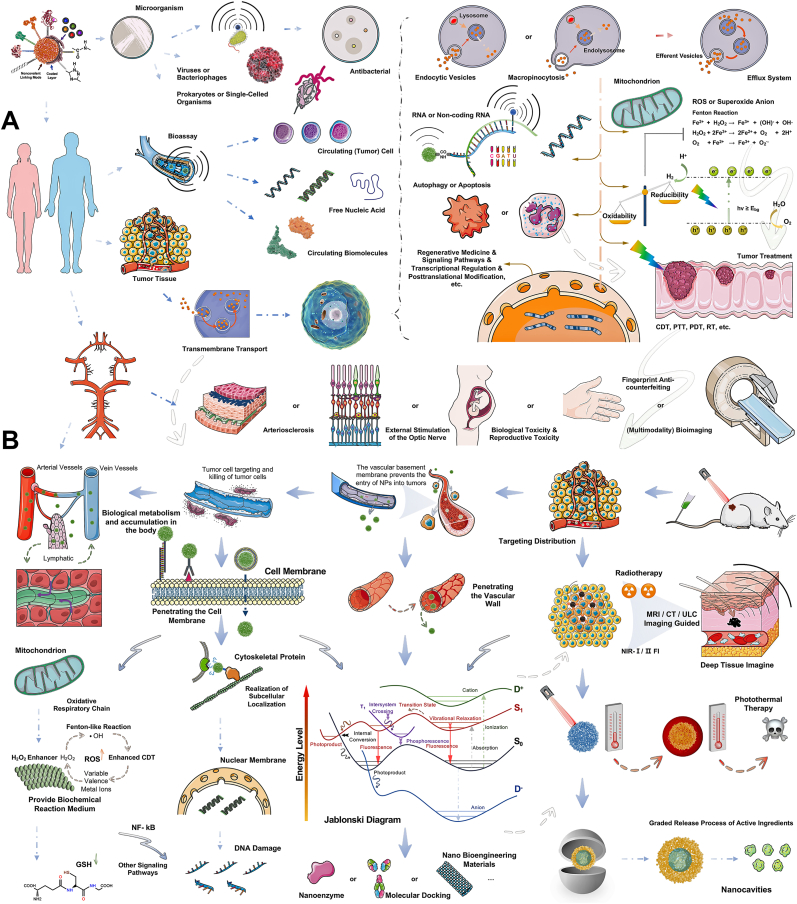
Fig. 8.
Strategies for the application of semiconducting polymer dots (Pdots) in biomedical fields, the mechanisms used in disease diagnosis & treatment, and the multimodal therapy. Upper Left). Strategy for detection of histological parameters based on Pdots. Upper Right). Schematic diagram of transmembrane transport modes of Pdots. When Pdots enter the target cells, they can trigger various biological behaviors, such as cell proliferation, autophagy, or apoptosis. In addition, a nanobiological interface for the Fenton Reaction can be provided to generate ROS through a cascade reaction. Combined with Pdots' thermal conversion and radiation generation ability, it can achieve multi-dimensional therapeutic effects on tumors. Middle Part). Biotoxicity and other clinical applications of Pdots. Left Lower). Realization of the targeting function and subcellular spatial localization of functionalized Pdots. Right Lower). Schematic diagram of nanomedicine's construction strategy and therapeutic effect based on Pdots. Abbreviations: CDT, Chemodynamic therapy; PDT, photodynamic therapy; PAI, photoacoustic imaging technology; GSH, glutathione; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; PTT, photothermal therapy; PTT-CDT, photothermal-chemodynamic therapy; ROS, reactive oxygen species; RT, radiotherapy; SDT, sonodynamic therapy.