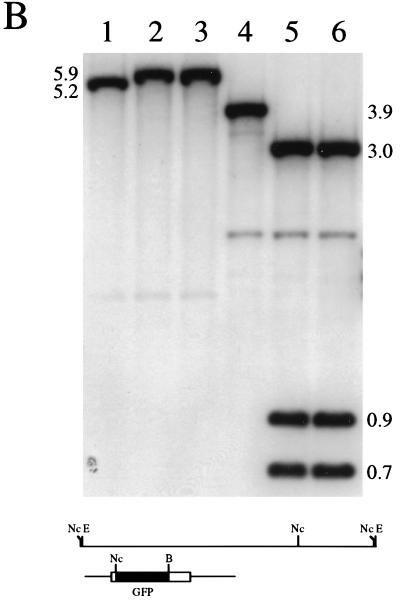
FIG. 3.
Marker rescue of VP26-GFP into the virus genome. Vero cells seeded at 3.5 × 104 cells/cm2 in culture dishes were transfected approximately 16 h later with KOS viral DNA (2 μg) and linearized pK26GFP (5 μg) (CellPhect; Pharmacia Upjohn). The transfection progeny was harvested 2 days later and plated for single plaques. Plaques were visualized in a fluorescence microscope, and the fluorescent plaques were picked and purified further. (A) One such virus, designated K26GFP-1, was plated on Vero cell monolayers, and a single plaque was photographed upon visualization in a fluorescence microscope (×10 objective). (B) Two micrograms of KOS (lanes 1 and 4), K26GFP-1 (lanes 2 and 5), and K26GFP-2 (lanes 3 and 6) was digested with EcoRI (lanes 1 to 3) or double digested with NcoI and BsrGI (lanes 4 to 6), the restriction fragments were resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis and transferred to nitrocellulose (Schleicher and Schuell), and the filters were probed with 32P-labeled pK26GFP. The diagram below the blot shows the EcoRI L region of HSV-1 strain KOS. The probe, pK26GFP, is shown below this. Relevant restriction sites are indicated: E, EcoRI; Nc, NcoI; and B, BsrGI. For details of autoradiograph scanning, see the legend for Fig. 4.