Fig. 6. Vascular- and clot-associated PAI-1 expression in COVID-19 lung autopsy samples.
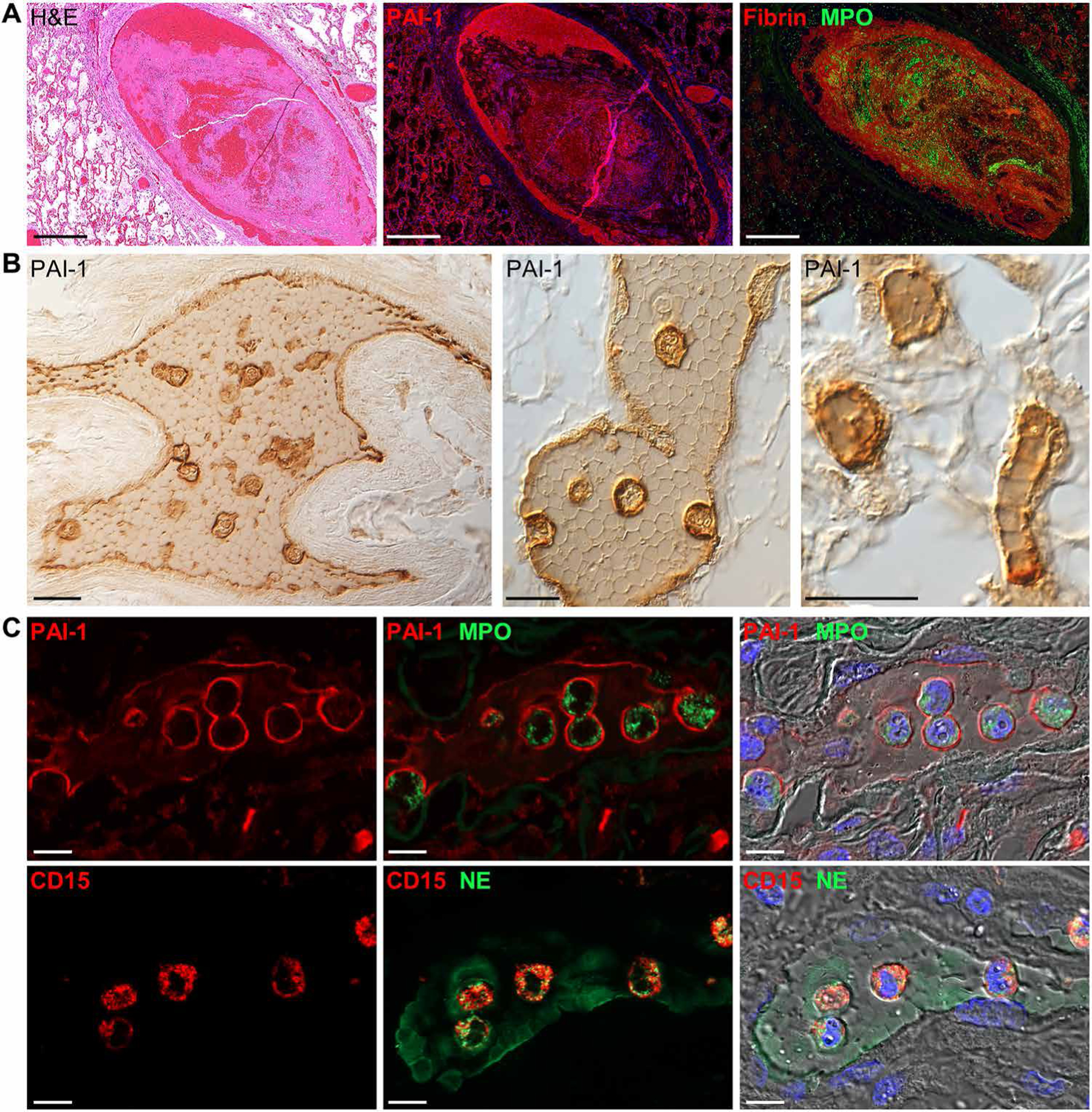
(A) Representative images of a pulmonary clot in lung tissue from a patient with COVID-19 (case 7). Serial lung sections were stained with H&E or were immunostained for PAI-1 or fibrin and MPO. Marked PAI-1 expression was observed along the inner endothelial lining and colocalized with fibrin-rich regions of the clot. (B) Representative immunohistochemical images of clot-associated PAI-1 expression in a medium-sized pulmonary artery (left), small-sized pulmonary vein (middle), and alveolar capillaries (right) (case 10). PAI-1 was detected on vessel endothelium and was lightly expressed between tightly packed polyhedrocyte-shaped red blood cells and markedly expressed on clot-embedded cells. (C) Shown are immunofluorescence and DIC images of clot-embedded cells expressing PAI-1 and the neutrophil markers, MPO, neutrophil elastase (NE), and CD15. Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33342 dye (blue). Scale bars, 500 μm (A) and 10 μm (B and C).
