Figure 2 .
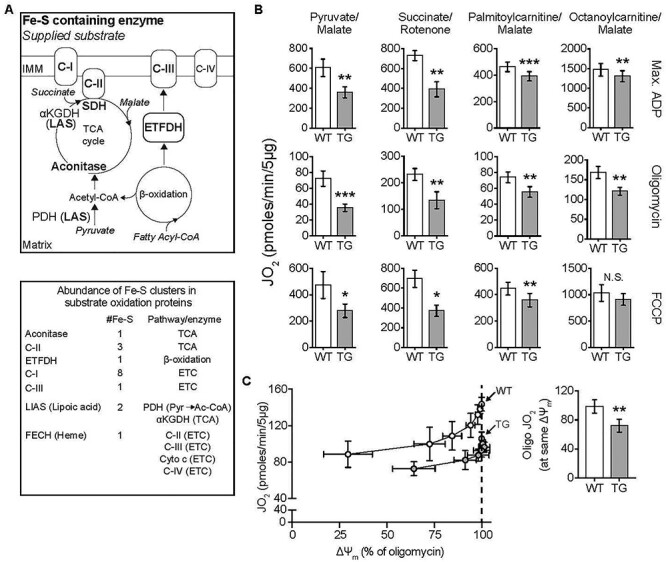
Substrate-dependent decrease in mitochondrial oxphos in TG hearts. All measurements were done in heart mitochondria from WT and TG mice fed Doxy for 18 weeks. (A) Upper: Diagram shows ISC-containing enzymes (bold font), and the substrates supplied in bioenergetics experiments (italics). Lower: List of ISC-containing complexes/enzymes with corresponding number of ISCs and associated metabolic pathway or enzyme. αKGDH: α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, Cyto c: Cytochrome c. C-I, C-II, CIII and C-IV are mitochondrial respiratory complexes I, II, III and IV. Pyr: pyruvate; Ac-CoA: acetyl-CoA. (B) Oxygen consumption rate (JO2) measured in isolated heart mitochondria supplied with pyruvate/malate (10 mM/5 mM), succinate (10 mM + 1 μM rotenone to prevent electron backflow through complex I), palmitoyl-L-carnitine plus malate (20 μM + 1 mM), or octanoyl-L-carnitine plus malate (200 μM + 1 mM). Max. ADP, saturating [ADP] (4 mM), was used to evaluate JO2 reflecting maximal oxphos. Oligomycin was used to evaluate JO2 that reflects maximal leak-dependent oxidation. The chemical uncoupler, FCCP (1 μM), 2.5 μg/ml) as used to evaluate JO2 that reflects maximal ETC capacity under the prevailing substrate conditions. N = 4–5/genotype except for octanoyl-L-carnitine (n = 4/genotype). (C) Proton leak was determined by measuring mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) and JO2 during antimycin (Complex III inhibitor) titration of octanoyl-L-carnitine oxidation, in the presence of oligomycin. Bar chart: JO2 values at the same ΔΨm (dashed line in the panel at left) (n = 3/genotype). B and C: Values are mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was by unpaired t-test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
