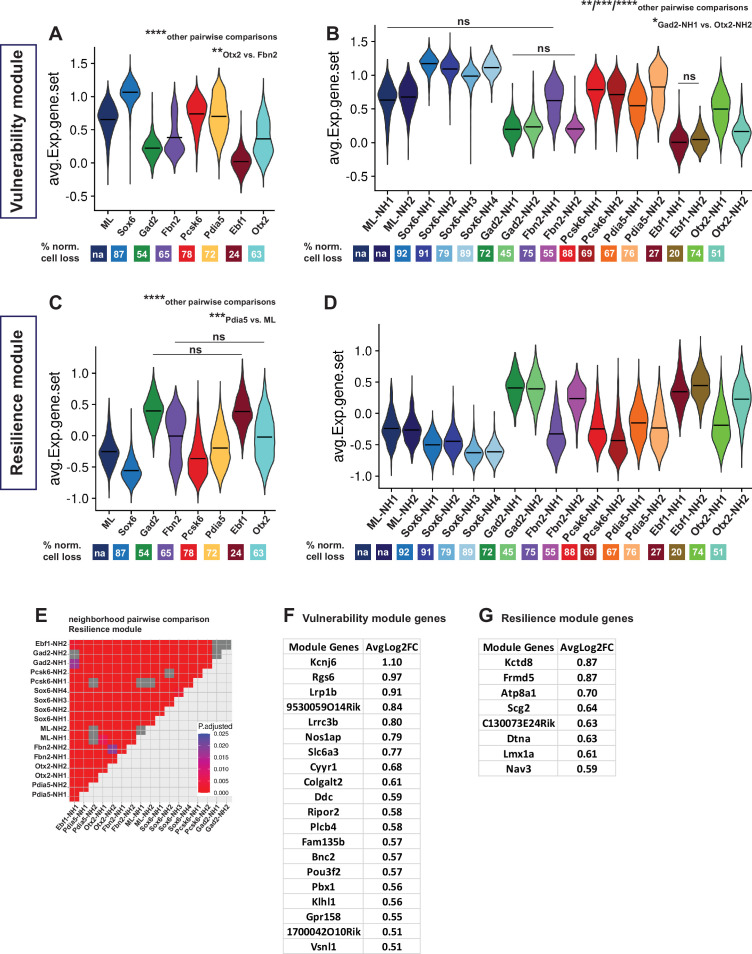
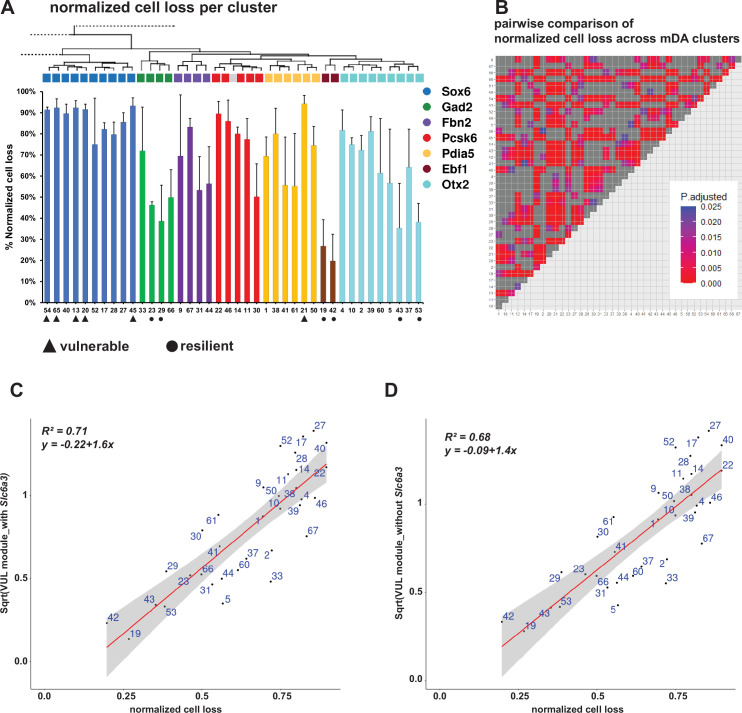
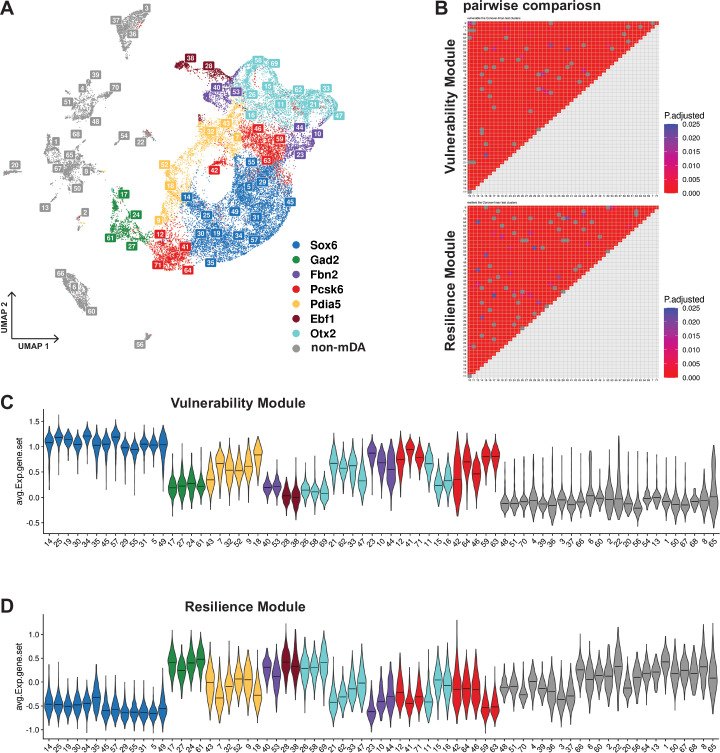
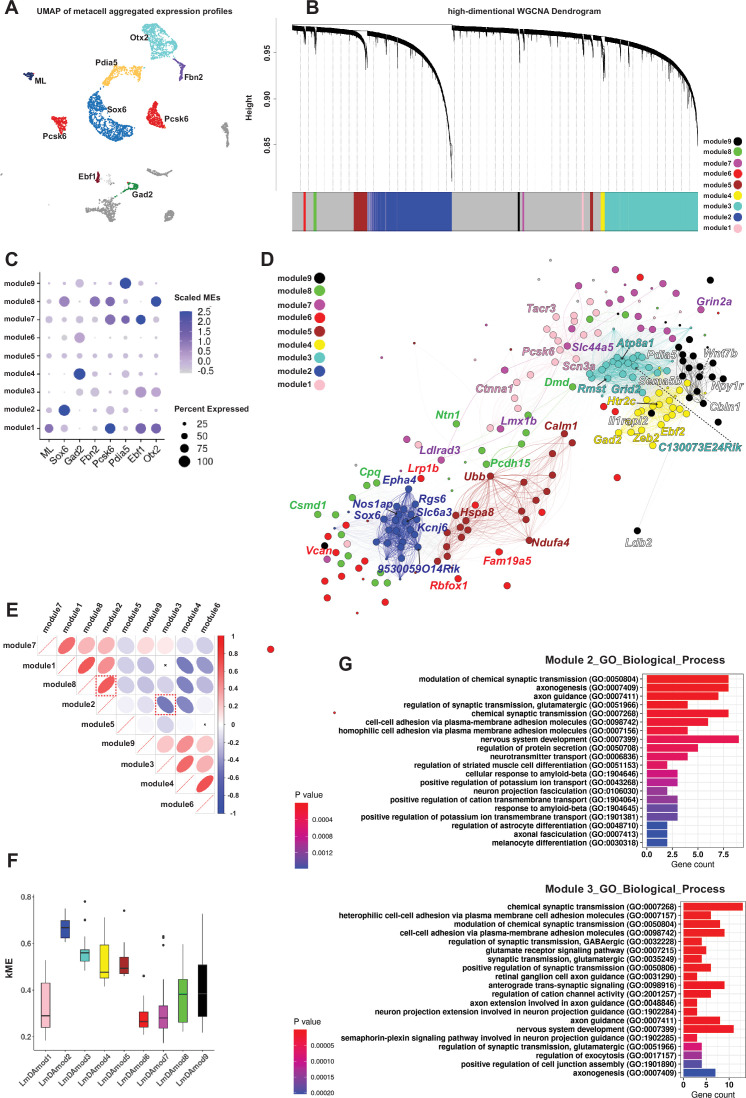
Figure 6. Vulnerability and resilience modules in territories, neighborhoods, and the ML clusters.
(A, B) Violin plots of the vulnerability module across territories and neighborhoods, with percentage of normalized cell loss shown at the bottom per territory and neighborhood, respectively. (C, D) Violin plots of the resilience module across territories and neighborhoods, with percentage of normalized cell loss shown at the bottom per territory and neighborhood, respectively. Pairwise comparisons of vulnerability module scores across territories and neighborhoods, respectively. (E) Pairwise comparisons of resilience module scores across neighborhoods. (F) Vulnerability module gene list, ranked by average Log2FC. (G) Resilience module gene list, ranked by average Log2FC. Summary statistics center lines are mean values. na = not applicable. ns = not significant. Sample size per condition (n) = 6. See Materials and methods for the statistical tests used.