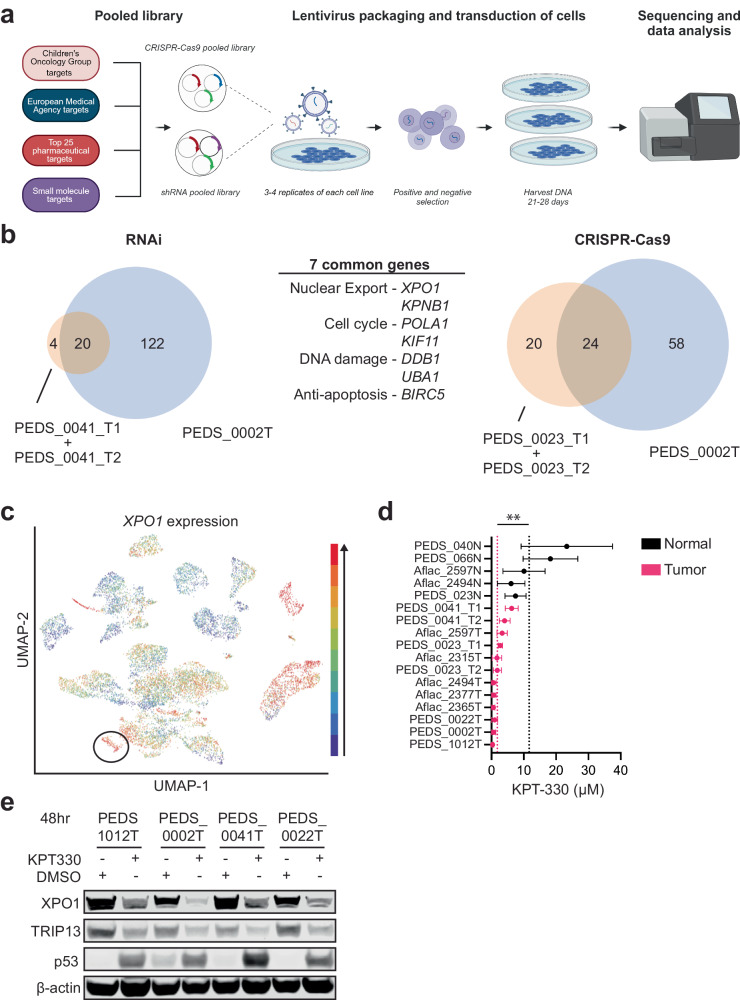
Fig. 3. XPO1 is a potential therapeutic target in Wilms tumor cells.
a Schematic outlining the methodology of CRISPR-Cas9 and RNAi functional screens. Created with BioRender.com. b RNAi suppression in three cell lines (patient-derived PEDS_0041_T1 and PDX-derived PEDS_0041_T2 cell lines are grouped together) identified 20 common genes which were critical for the survival of WT cells. CRISPR-Cas9 screens identified 24 common genes in three cell lines (patient-derived PEDS_0023_T1 and PDX-derived PEDS_0023T_T2 cell lines are grouped together), which were critical for the survival of WT cells. Seven genes overlapped between the RNAi and CRISPR-Cas9 loss-of-function screens. These seven genes can be categorized under their role in nuclear export, cell cycle, DNA damage, and apoptosis. c UCSC Treehouse transcriptional data from 12,719 samples showing expression of XPO1 in all tumor types with WT samples circled in black. Blue to red colors signify expression levels with red being the highest among this cohort. d Forest plot representing the mean IC50 of KPT-330 in the panel of WT cell lines and normal cells (ending with N). SD shown from at least two biological replicates. **P value < 0.005 from a Student’s two-tailed unpaired t test. e Immunoblots depicting the decrease in total protein levels of XPO1 and TRIP13 upon treatment with KPT-330. Data shown are representative of two biological replicates.