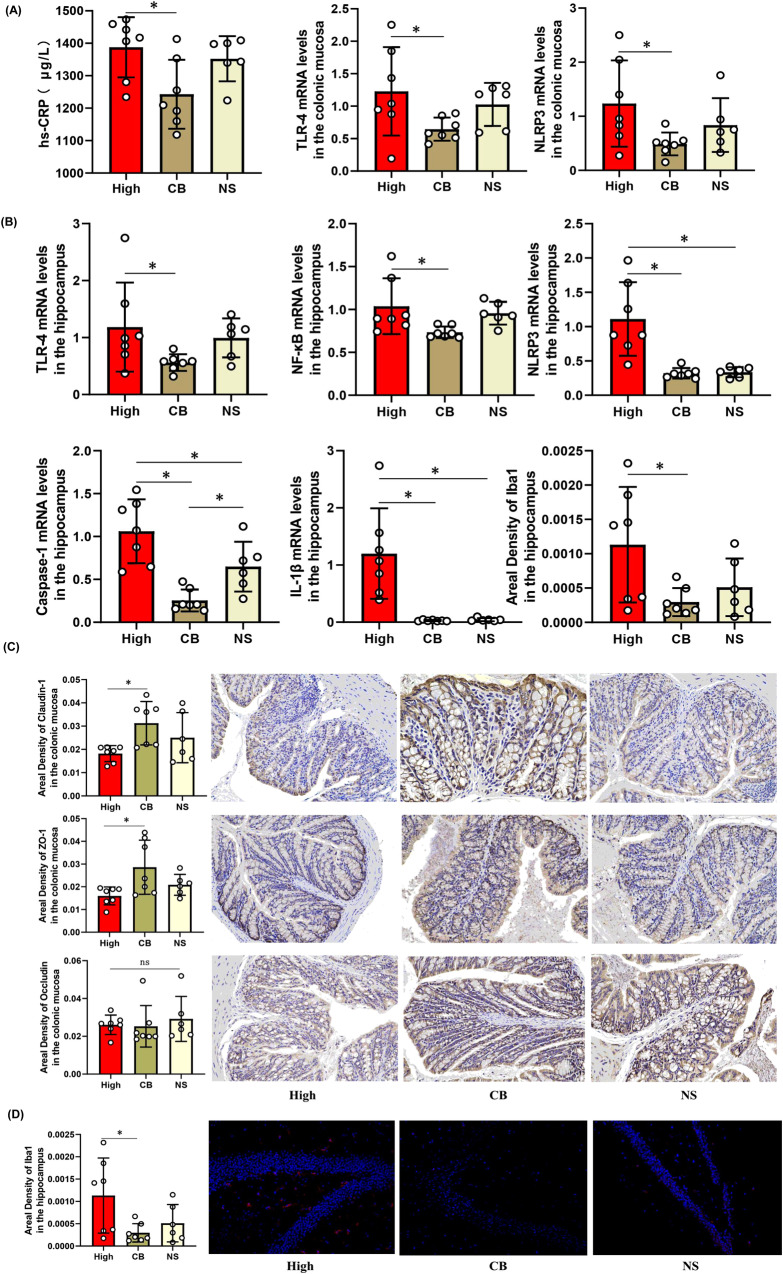
Fig. 7. Effects of probiotics (CB) on inflammatory factors of the mouse model of inflammatory depression.
A The CB decreased the expression of TLR-4 (P = 0.018), NLRP3(P = 0.023) in the intestinal mucosa and the concentration of hs-CRP in the serum (P = 0.024). (n/High inflammatory group = 7, n/CB group = 7, n/NS group = 6). B The CB decreased the expression of TLR-4(P = 0.048), NF-κB(P = 0.041), NLRP3(P < 0.001) and Caspase-1(P < 0.001) in the brain. C The amount and area density of permeability biomakers such as Claudin-1(P = 0.030), ZO-1(P = 0.026) were increased in the CB group by ELISA and immunohistochemistry (×400 magnificent).The area density of Occludin tended to increase, but there was no statistical difference (P = 0.750). D The area density, amount and branch of microglia in hippocampus were decreased in the CB group (P = 0.034). One-way ANOVA test for multiple comparisons with Tukey’s test for post hoc corrections. Data are presented as mean values with SD. Scatter plot indicate median and error range. The upper and lower whiskers indicate median ± SD. P-value is marked as follows: *P ≤ 0.05. ns indicates non-significant. All statistical tests are two-sided. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.