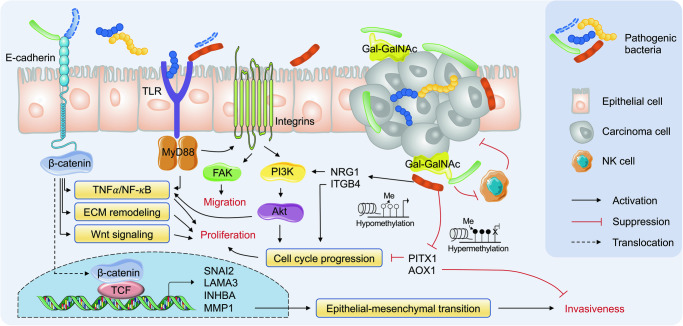
Fig. 6. Schematic model hypothesizing the carcinogenetic potential of pathogenic bacteria in OSCC pathogenesis.
F. nucleatum virulence factor FadA has been reported to activate the E-cadherin/β-catenin associated cell signaling, which further activates the TNFα/NF-κB proinflammatory pathway, ECM remodeling, and Wnt signaling. Subsequently, β-catenin can be translocated to the nucleus to form a complex with T-cell factor protein (TCF) and activate EMT-related genes, such as SNAI2, LAMA3, INHBA, and MMP1. Moreover, F. nucleatum and T. denticola have been reported to promote cancer aggressivity via crosstalk between the integrin/FAK and TLR/MyD88 signaling pathways. Integrin-associated PI3K/Akt signaling can be activated by P. anaerobius, which regulates cell cycle progression. Gal-GalNAc on tumor cells is the receptor of Fap2 to recruit F. nucleatum to the tumor site. In addition, hypomethylation of NRG1 may activate the PI3K/AKT pathway while hypermethylation of AOX1 may promote cellular invasion and metastasis.