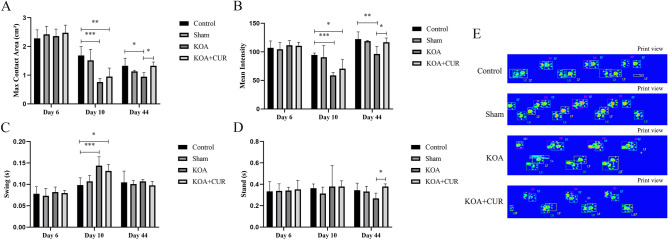
Figure 2.
CUR ameliorates gait abnormalities in rats caused by KOA. (A) Effect of KOA on the maximum contact area of rats. Maximum contact area (cm2) represents the maximum surface area of the claw in contact with the glass plate. (B) Effect of KOA on the mean intensity of rats. Mean intensity represents the average intensity of the claw in contact with the glass plate. (C) Effect of KOA on the swing of rats. Swing (s) is the time that the claw did not make contact with the glass plate during a walking cycle. (D) Effect of KOA on the stand of rats. Stand (s) is the time that the claw is in contact with the glass plate. (E) This is the print view of the claw on the glass plate. Control represents the blank control rats. Sham represents sham-operated group rats. KOA represents the knee osteoarthritis model group rats. KOA + CUR represents the treated group rats with feeding CUR. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. All data are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 8 for each group.