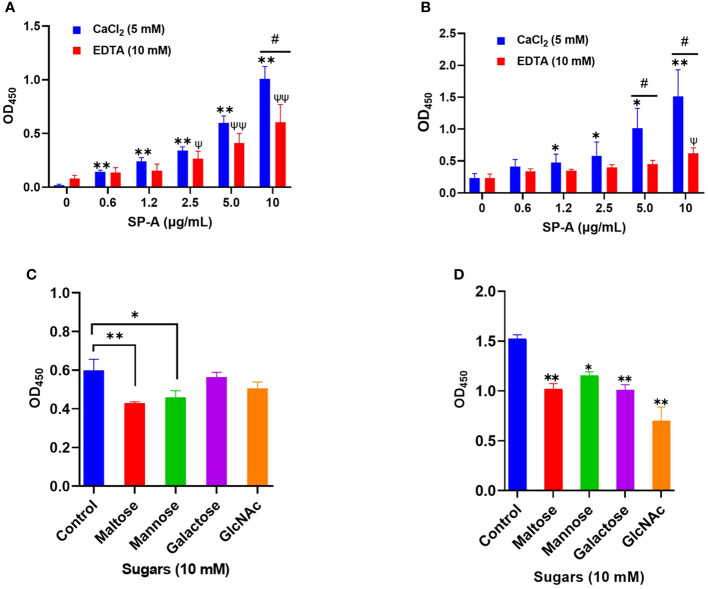
Figure 1.
Human SP-A interacts with SARS-CoV-2 S protein and RBD. Purified S protein and RBD was immobilized on ELISA plates followed by incubation with serial dilutions of SP-A (0-10 μg/ml) in either 5 mM CaCl2 or 10 mM EDTA-containing buffer. The data show a dose-dependent increase in SP-A binding to SARS-CoV-2 S protein (A) and RBD (B). SARS-CoV-2 S protein (C) and RBD (D) coated plates were incubated with 10 μg/ml SP-A in the presence of 10 mM of each kind of sugar i.e. maltose, mannose, galactose, and N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc). Control samples were incubated, with SP-A in 5 mM CaCl2 buffer without sugars and absorbance readings compared to control samples. Experiments were carried out in duplicates with three independent experiments. The data are presented as mean ± SE of 3 independent experiments. (*P<0.05; **P<0.01 reflect the levels of statistical significance in comparison with no SP-A treated group (0 μg/ml) in 5 mM CaCl2-containing buffer by unpaired student’s t-test analysis. ψ<0.05, ψψ<0.01 are the levels of significance compared to 0 μg/ml SP-A in 10 mM EDTA buffer while #<0.05 is the level of significance for the same SP-A concentrations in 5 mM CaCl2 vs 10 mM EDTA-containing groups.