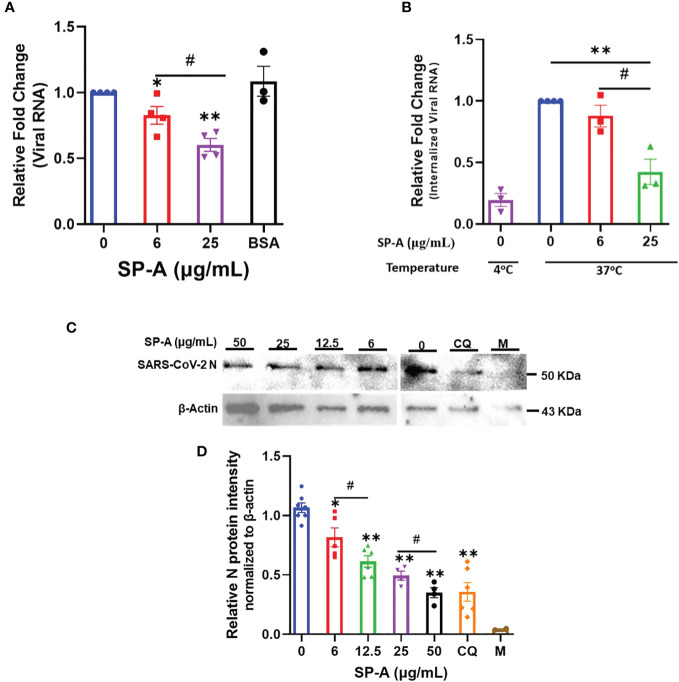
Figure 4.
SP-A attenuates SARS-CoV-2 (Delta) binding and entry in A549-ACE2 cells. (A) Viral binding assays were performed in A549-ACE2 cells. SARS-CoV-2 (Delta variant) was pre-incubated with the indicated concentrations of SP-A or BSA (used as a non-specific protein control, 50 μg/ml) for 1h at RT. Then inoculated onto pre-chilled cells for another 2 h at 4°C to allow binding to the cell surface. (B) Viral entry assays were performed as described above. However, after 2 h incubation of SP-A + virus mixture at 4°C, the cells were washed, and fresh media was added and shifted to 37°C for 1 h to allow virus entry into cells. The cells were washed and treated with proteinase K (1 mg/ml) to remove attached viral particles on the cell surface and the amount of internalized viral particles was quantified by RT-qPCR. Binding control at 4°C was also used to assess virus entry by treating cells inoculated with virus only (0 μg/ml SP-A) after 2 h incubation with proteinase K prior to shifting to 37°C. The relative fold change was normalized to 18S rRNA internal control and expressed as mean ± SEM of the relative fold change in CT values compared to the control sample (0 μg/ml). (C) A549-ACE2 cells inoculated with SP-A + virus mixture for 2h and then cells were harvested after 4 h incubation for Western blotting analysis using SARS-CoV-2 N protein and β-actin antibodies, respectively. Representative images of Western blotting analysis of cell lysates with SARS-CoV-2 N protein and β-actin as a control. Chloroquine (CQ) (10 µM) was used as a positive control. (D) Quantification of N protein level relative to β-actin (loading control). Each data represents the relative mean ± S.E. *P<0.05; **P<0.01, compared to control group (0 μg/ml); #<0.05= significance between two doses.