Fig. 4.
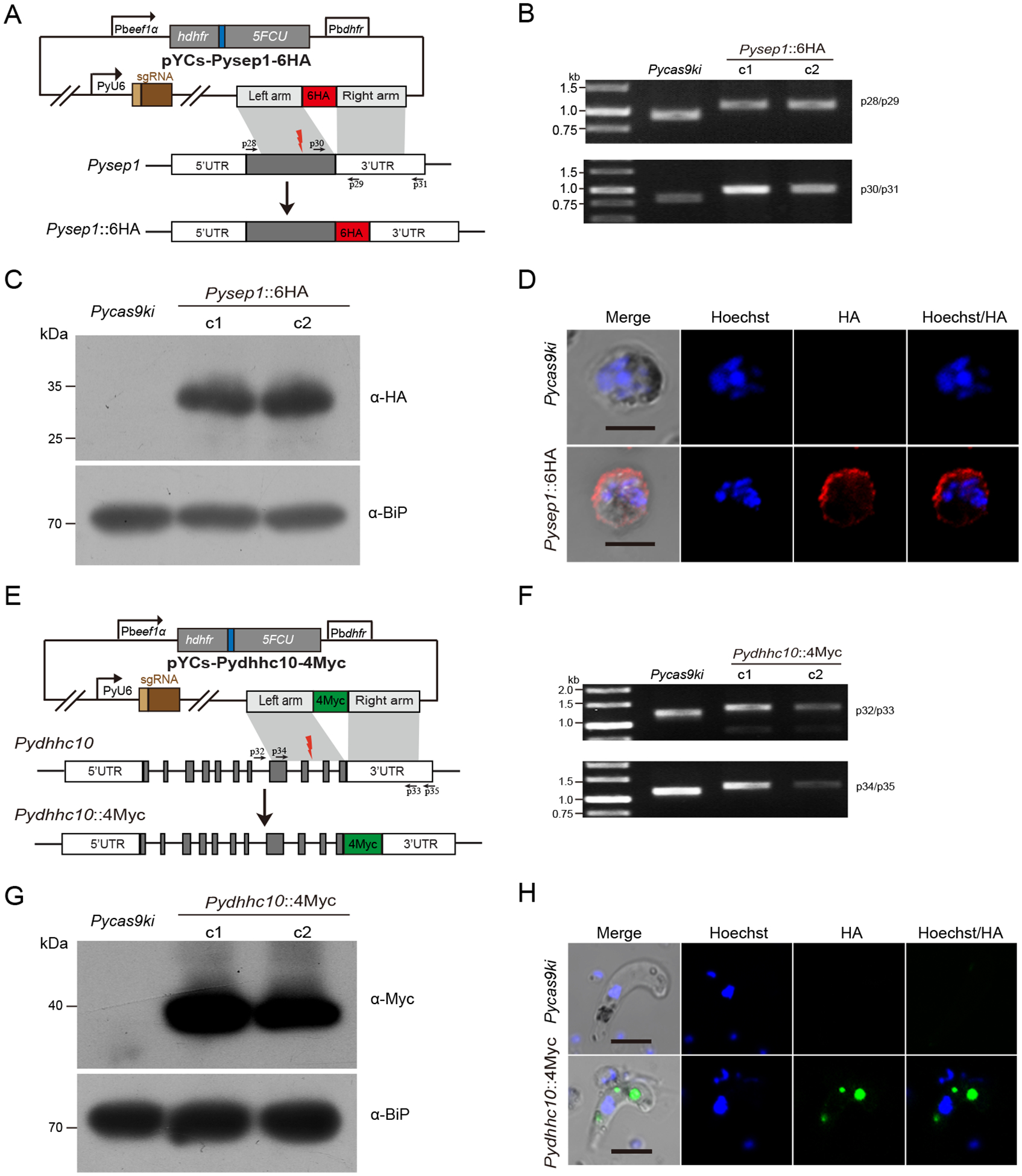
Tagging and protein expression of endogenous sep1 and dhhc10 genes in the PyCas9ki parasite
A. Schematic diagram of pYCs construct for tagging the sep1 gene with 6HA. The site for designed sgRNA recognition was indicated as red thunderbolt.
B. PCR detection of the PyCas9ki parasite and two PyCas9ki derived clones with sep1 gene tagging with 6HA C-terminally.
C. Western blotting analysis of 6HA tagged Sep1 protein expression in the asexual blood stage of the PyCas9ki parasite and two PyCas9ki derived clones. Anti-HA antibody was used for the detection. BiP protein serves as an internal control.
D. IFA analysis of 6HA tagged Sep1 protein expression in the asexual blood stage of the PyCas9ki parasite and one PyCas9ki derived clones. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst33342 (blue). Bar = 5 μm.
E. Schematic diagram of pYCs construct for tagging the dhhc10 gene with 4Myc. The site for designed sgRNA recognition was indicated as red thunderbolt.
F. PCR detection of the PyCas9ki parasite and two PyCas9ki derived clones with dhhc10 gene tagging with 4Myc C-terminally.
G. Western blotting analysis of the 4Myc tagged DHHC10 protein expression in the ookinetes of the PyCas9ki parasite and two PyCas9ki derived clones. Anti-Myc antibody was used for the detection. BiP protein serves as an internal control.
H. IFA analysis of the 4Myc tagged DHHC10 protein expression in the ookinetes of the PyCas9ki parasite and one PyCas9ki derived clones. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst33342 (blue). Bar = 5 μm.
