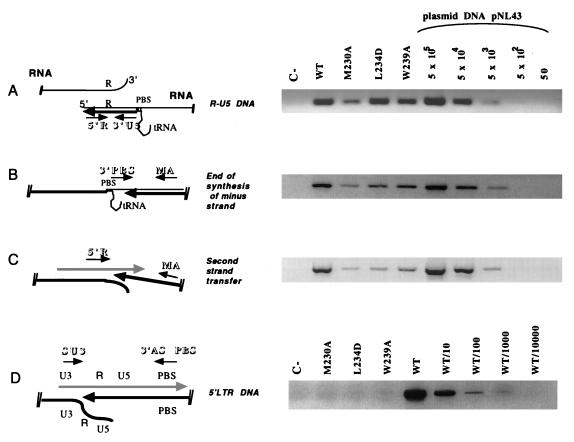
FIG. 4.
Early and late phases of proviral DNA synthesis analyzed by PCR. HeLa P4 cells were infected for 18 h with WT or mutant viral supernatant. Extrachromosomal DNA was prepared by the method described by Hirt (12), and a fraction (corresponding to 105 cells infected with 1 ml of viral supernatant) was subjected to each PCR amplification with alternative primer pairs for determination of early and late steps of reverse transcription. (The localization of each primer pair relative to the viral genome is schematically represented on the left of each panel.) The primer pairs used were 5′R/3′U5 (5′R, 5′-GGTCTCTCTGGTTAGACCA-3′; 3′U5, 5′-CTGCTAGAGATTTTCCACAC-3′) for R-U5 DNA corresponding to the earliest stage of reverse transcription (A); 3′PBS/MA (3′PBS, 5′-ACTTGAAAGCGAAAGTAAAGC-3′; and MA, 5′-GGTCTCTCTGGTTAGACCA-3′) for extended minus-strand DNA (B); 5′R/MA (5′R, 5′-GGTCTCTCTGGTTAGACCA-3′; MA, 5′-GGTCTCTCTGGTTAGACCA-3′) for plus-strand DNA synthesized just after second-strand transfer (C); and SU3/ASPBS (SU3, 5′-GCACCATCCAAAGGTCAGTGG-3′; ASPBS, 5′-CTCCTCTGGCTTTACTTTCGC-3′) to detect synthesis of the 5′ LTR DNA. The absence of contaminating pNL4-3 plasmid in the samples was confirmed by using primers localized within the flanking (5′check) and the pUC (3′check) sequences of the plasmid (not shown). PCR products were resolved on a 1.5% agarose gel and were visualized by ethidium bromide staining. For PCR amplifications A, B, and C, serial dilutions of the plasmid pNL4-3 (corresponding to 50 to 5 × 105 copies) were used as a positive control and a basis for quantification. Since pNL4-3 contains a hybrid provirus with sequence mismatches between the 5′ LTR and the 3′ LTR, the primer pair 5′SU3/3′ASPBS can amplify only synthesized viral DNA and not the plasmid. Consequently, we used dilutions of the WT sample as the control set for the 5′ LTR proviral DNA amplification (D). In the schematic diagrams, RNA is represented by thin lines, minus-strand DNA is indicated by thick black lines, and plus-strand DNA is indicated by hatched thick lines. Arrows indicate the directions of synthesis, while small arrows represent primers.