Table 1.
Case allocation from 2016 World Health Organization classification to 2022 International Consensus Classification and 2022 World Health Organization classification of 635 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes/neoplasms.
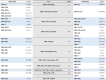 |
AML acute myeloid leukemia, EB excess of blasts, ICC International Consensus Classification, MDS myelodysplastic syndromes/neoplasms, MDS-RS MDS with ring sideroblasts, MDS-EB MDS with excess blasts, MDS-SLD MDS with single lineage dysplasia, MDS-MLD MDS with multilineage dysplasia, MDS-RS-SLD MDS with ring sideroblasts and single lineage dysplasia, MDS-RS-MLD MDS with ring sideroblasts and multilineage dysplasia, MDS-U MDS, unclassifiable, MDS-5q MDS with low blasts and isolated 5q deletion, MDS-SF3B1 MDS with low blasts and SF3B1 mutation, MDS-LB and RS MDS with low blasts and ring sideroblasts, MDS-LB MDS with low blasts, MDS-h hypoplastic MDS, MDS-IB1 MDS with increased blasts-1, MDS-IB2 MDS with increased blasts-2, MDS-f MDS with fibrosis, MDS-biTP53 MDS with biallelic TP53 inactivation, NOS not otherwise specified, WHO World Health Organization.
*MDS-related gene mutations: ASXL1, BCOR, EZH2, RUNX1, SF3B1, SRSF2, STAG2, U2AF1, or ZRSR2.
†MDS-related cytogenetic abnormalities: complex (≥3 clones) karyotype (in the absence of a TP53 mutation), del(5q)/t(5q)/add(5q), -7/del(7q), +8, del(12p)/t(12p)/add(12p), i(17q), -17/add(17p) or del(17p), del(20q), and/or idic(X)(q13) clonal abnormalities.
