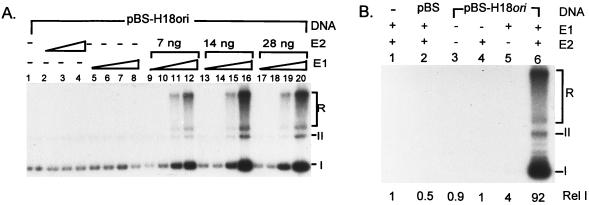
FIG. 3.
HPV-18 ori replication in the presence of E1 and E2 fusion proteins. In this and subsequent figures, cell-free replication was conducted with 100 μg of 293 cell extracts and 0 or 40 ng of template DNA (pBS-H18ori or pBS). (A) Effects of E1 and E2 protein concentrations on HPV-18 ori replication. Cell-free replication reaction mixtures containing 40 ng of pBSH18ori (all lanes) were conducted in the absence of His-H18E1 and GST-H18E2 (lane 1), in the presence of GST-H18E2 alone (lanes 2 to 4), in the presence of His-H18E1 alone (lanes 5 to 8), or in the presence of both His-H18E1 and GST-H18E2 (lanes 9 to 20). The amount of E1 fusion protein in the reaction mixtures was 22.5 ng (lanes 5, 9, 13, and 17), 45 ng (lanes 6, 10, 14, and 18), 90 ng (lanes 7, 11, 15, and 19), or 180 ng (lanes 8, 12, 16, and 20). The amount of GST-H18E2 protein was 7 ng (lanes 2 and 9 to 12), 14 ng (lanes 3 and 13 to 16), or 28 ng (lanes 4 and 17 to 20). (B) Specificity of cell-free HPV-18 ori replication under optimal conditions as defined for panel A. Replication was conducted in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 180 ng of His-H18E1 and 14 ng of GST-H18E2 as indicated (lanes 2 to 6). form I (I), form II (II), and replication intermediates (R) are marked here and in Fig. 4 through 7. Incorporation in the absence of E1, E2, or both was due to repair synthesis, as evidenced by the lack of slow-migrating replication intermediates. The relative [α-32P]dCTP incorporation of each reaction was quantified by using a PhosphorImager. The relative intensity (Rel I) was calculated by comparing isotope incorporation to that in lane 1 (with no exogenous DNA template).