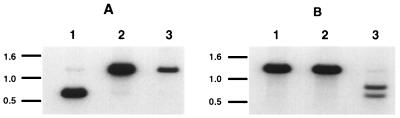
FIG. 1.
Southern blot analysis of the mutant KgB(C633S) and KgB(C596S/C633S) viruses. An NcoI-digested 1,305-bp fragment from gB was 32P labeled and used to Southern blot viral DNA from KOS (lanes 1), KgB(C633S) (lanes 2), and KgB(C596S/C633S) (lanes 3). These viral DNA samples were digested with NcoI and ApaLI (A) or RmaI (B). (A) The [32P]gB probe hybridized with two fragments of 639 and 666 bp in KOS-digested DNA (lane 1, two indistinguishable bands on this gel) and hybridized with one fragment of 1,305 bp in KgB(C633S)- and KgB(C596S/C633S)-digested DNA, indicating the loss of an ApaLI restriction site marking the gB mutation at amino acid 633. (B) The same [32P]gB probe hybridized to a fragment of 1,259 bp in KOS-digested DNA (lane 1) as well as KgB(C633S)-digested DNA (lanes 2) and hybridized to two fragments of 724 and 535 bp in KgB(C596S/C633S)-digested DNA (lane 3), marking the insertion of an RmaI restriction site and the gB mutation at amino acid 596. Positions of migration of the DNA standard are marked in kilobases on each panel.