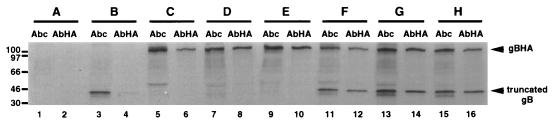
FIG. 3.
Ability of mutant gB molecules to form hetero-oligomers. Vero cell monolayers were mock transfected (lanes 1 and 2) or transfected individually with a plasmid encoding a truncated gB molecule (pKΔ5C; lanes 3 and 4), HA-tagged gB molecule (gBHA; lanes 5 and 6), or recombinant HA-tagged gB molecules [gBHA(C633S) or gBHA(C596S/C633S); lanes 7 and 8 or lanes 9 and 10, respectively]. Monolayers were also cotransfected with a plasmid encoding the truncated gB molecule (pKΔ5C) and gBHA (lanes 11 and 12), gBHA(C633S) (lanes 13 and 14), or gBHA(C596S/C633S)S (lanes 15 and 16). Twenty-four hours posttransfection, cells were infected with a gB-deleted virus (KΔ4BX) at an MOI of 10 in the presence of [35S]methionine-cysteine. Seven hours p.i., cell monolayers were harvested and immunoprecipitated with a polyclonal antibody directed against the carboxy-terminal region of gB (Abc; lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, and 15) or anti-HA antibody (AbHA; lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, and 16). The protein A-Sepharose immunocomplexes were separated by SDS-PAGE. The positions of the HA-tagged wild-type and mutant gB molecules (all gBHA) as well as the truncated gB molecule are marked at the right. Molecular size markers are indicated in kilodaltons at the left of the figure.