Figure 6.
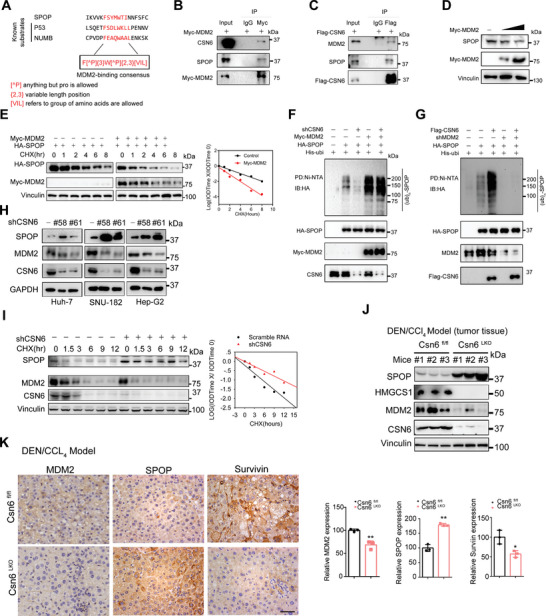
CSN6‐MDM2‐SPOP axis is involved in HMGCS1 dysregulation. A) Amino acid sequence alignment of putative MDM2 binding consensus motifs in SPOP. P53 and NUMB are known MDM2 substrates containing well‐characterized consensus motifs. B) Protein–protein interaction was assayed by co‐IP experiments using indicated antibodies. MDM2 interacts with CSN6 and SPOP. C) Protein‐protein interaction was assayed by co‐IP experiments using indicated antibodies. CSN6 interacts with MDM2 and SPOP. D) MDM2 overexpression decreases SPOP expression. E) Representative immunoblots showing SPOP protein turnover rate in 293T cells treated with CHX, in the presence of MDM2. MDM2 overexpression increased the turnover rate of SPOP. F,G) Immunoblot analysis of SPOP ubiquitination from 293T cells transfected with the indicated constructs and treated with MG132 for 6 h. H) Representative immunoblots showing SPOP and MDM2 expression in cancer cells transfected with shCSN6. Silencing CSN6 increased SPOP steady‐state expression in liver cancer cell lines. I) Representative immunoblots showing SPOP and MDM2 protein turnover rate in 293T cells treated with CHX (left), in the presence of shCSN6. Silencing CSN6 decreased SPOP protein turnover rates. J) Immunoblot analysis of indicated proteins in liver tissues of Csn6 fl/fl and Csn6 LKO mice. K) CSN6 depletion leads to decreased MDM2 expression and increased SPOP protein expression. Scale bar, 50 µm. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; n = 3.
