Figure 2. Polar network in the orthosteric binding pocket (OBP) of DRD1.
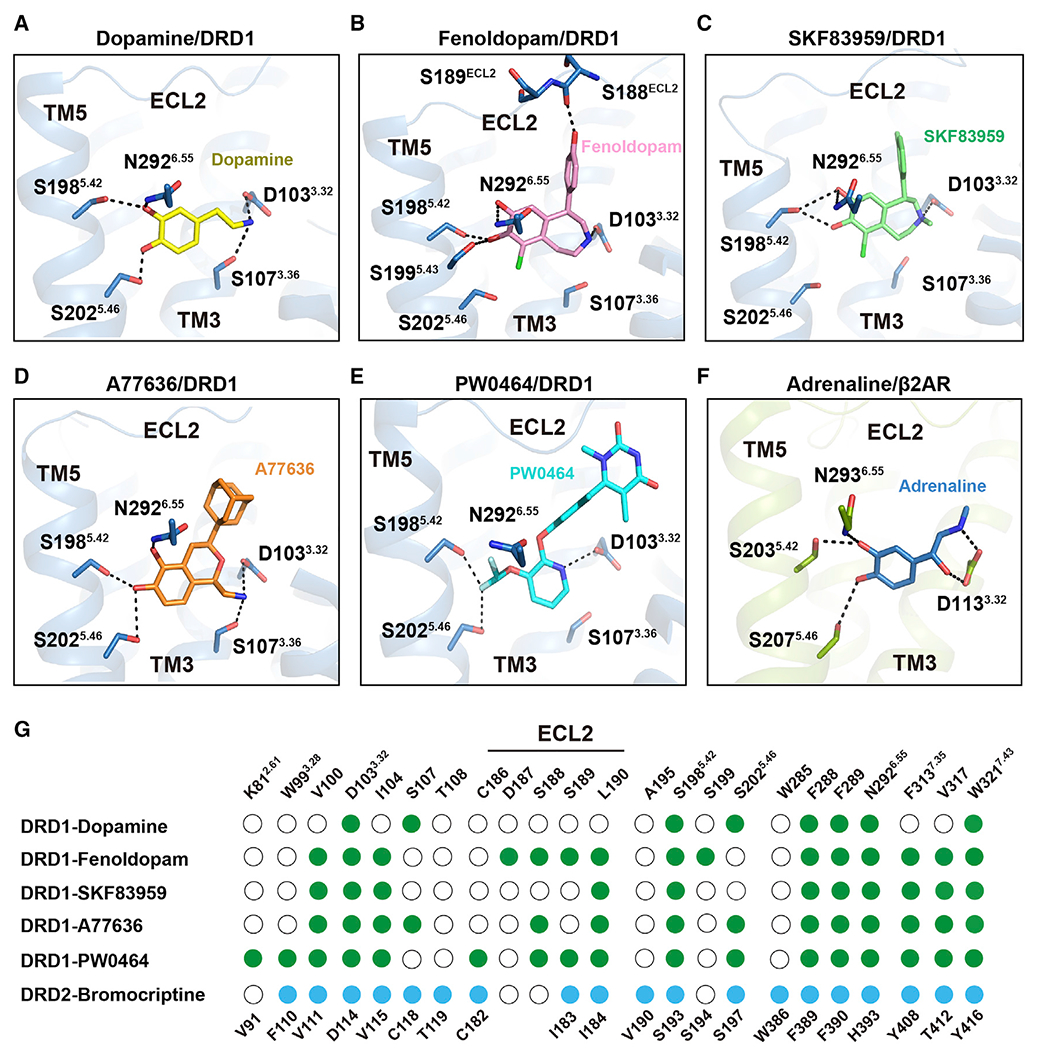
(A) Detailed interactions of dopamine (yellow) with DRD1 (sky blue); the hydroxyl groups of dopamine form potential polar interactions with the side chains of S1985.42, S2025.46, and N2926.55, and the amine group of dopamine forms salt bridges and hydrogen bond with D1033.32 and S1073.36 in DRD1, respectively. Polar interactions are highlighted as black dashed lines.
(B–E) Detailed interactions of fenoldopam (pink), SKF83959 (lime), A77636 (orange), and PW0464 (cyan) with DRD1 (sky blue). The polar interactions are indicated by black dashed lines.
(F) Detailed interactions of adrenaline (sky blue) with β2AR (limon) (PDB: 4LDO). The polar interactions are shown as black dashed lines.
(G) Comparison of agonist binding sites between DRD1 and DRD2. Residues in agonist-bound DRD1 or DRD2 that interact with ligands are indicated with green or blue dots, respectively. Residues that show no interaction with ligands are shown as white circles. Residue positions for DRD1 or DRD2 are indicated on the top or bottom of the scheme, respectively. Ballesteros-Weinstein numbers of D3.32-S5.42-S5.46, K2.61-W3.28-W7.43, or N6.55-F7.35 motif residues are shown as superscripts.
See also Figures S2 and S3 and Tables S2, S3 and S5.
