Figure 5. Binding of the PAM LY3154207 to DRD1.
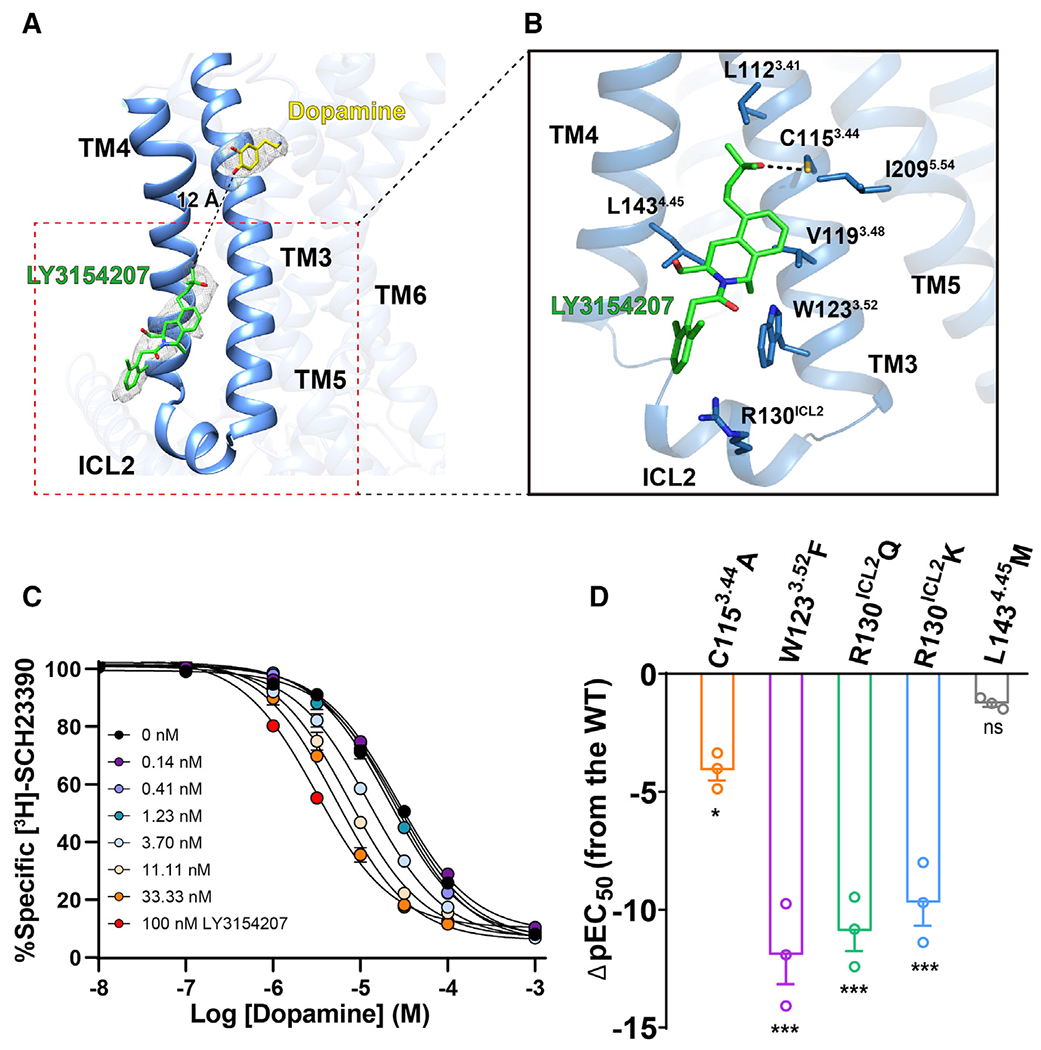
(A) Overall structure of DRD1 bound to dopamine (yellow stick) and LY3154207 (green stick). The structure reveals that an EM density (gray mesh, contoured at 0.022) corresponding to LY3154207 located at the membrane-embedded binding site was created by ICL2, TM3, and TM4, and the allosteric site in DRD1 is 12 Å away from the orthosteric site.
(B) Contact residues in dopamine-LY3154207-DRD1-Gs complex (sticks with sky-blue carbons) within 4 Å of the LY3154207 (green). Polar interaction is highlighted as a black dotted line.
(C) Competition binding curve of dopamine to wild-type (WT) DRD1 in the presence of different concentrations of LY3154207 (0.14–100 nM). LY3154207 enhanced the binding affinity of dopamine with DRD1. The Ki value (±SEM) of DRD1 for dopamine is 25.86 ± 1.9 μM, whereas the Ki value decreases to 3.16 ± 0.3 μM in the presence of 100 nM LY3154207. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three or more experiments run in triplicate.
(D) Dopamine-induced cAMP accumulation assay in the presence of 100 nM LY3154207. Bars represent differences in calculated potency of dopamine (ρEC50 [half maximal effective concentration]) for each mutation relative to WT of DRD1. *p < 0.01, ***p < 0.0001 (one-way analysis of variance [ANOVA] followed by the Dunnett’s test, compared with the response of WT).
See also Figure S6.
