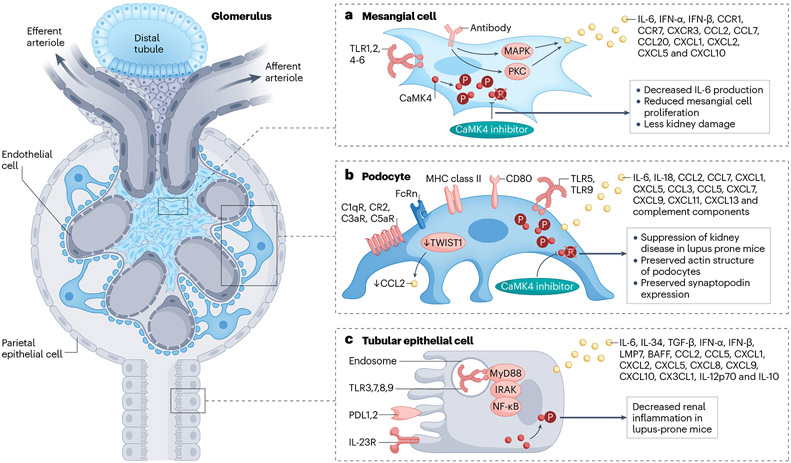
Fig. 2 ∣. Immune features of kidney parenchymal cells.
Kidney parenchymal cells, including podocytes, tubular epithelial cells and mesangial cells, express molecules that are typical of the innate and adaptive immune systems. These molecules have important roles in the recruitment of immune cells and in the development of inflammatory responses. a, Mesangial cells have long been known to express cytokines and chemokines in response to circulating inflammatory signals. For example, IL-6 can independently cause mesangial proliferation. Signalling molecules, such as CaMK4, may control the production of cytokines, and may therefore represent a treatment target. b, Podocytes produce and express molecules typically produced by cells of the immune system, including HLA, costimulatory molecules, the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), TLRs, and chemokines and their receptors, along with complement components and receptors. The transcription factor TWIST1 may suppress the production of CCL2 in healthy glomeruli. Podocyte injury may lead to the altered expression of molecules such as CaMK4, which can directly compromise the expression of molecules involved in their function (e.g. nephrin) or structure (e.g. synaptopodin). c, Similarly, TECs may produce cytokines and chemokines and their receptors, which may promote the recruitment of inflammatory cells. Such cells may, through the further production of cytokines, contribute to the damage of TECs. Again, alterations in the expression of molecules such as CaMK4 may contribute to the accumulation of immune cells and may therefore representa therapeutic target. FcRn, neonatal Fc receptor; TLR, Toll-like receptor; PDL1, programmed death ligand 1; IRAK, IL-1 receptor-associated kinase; TRAF6, TNF receptor-associated factor 6; BAFF, B cell–activating factor; LMP7, low–molecular mass polypeptide-7; CAMK4, calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase IV.