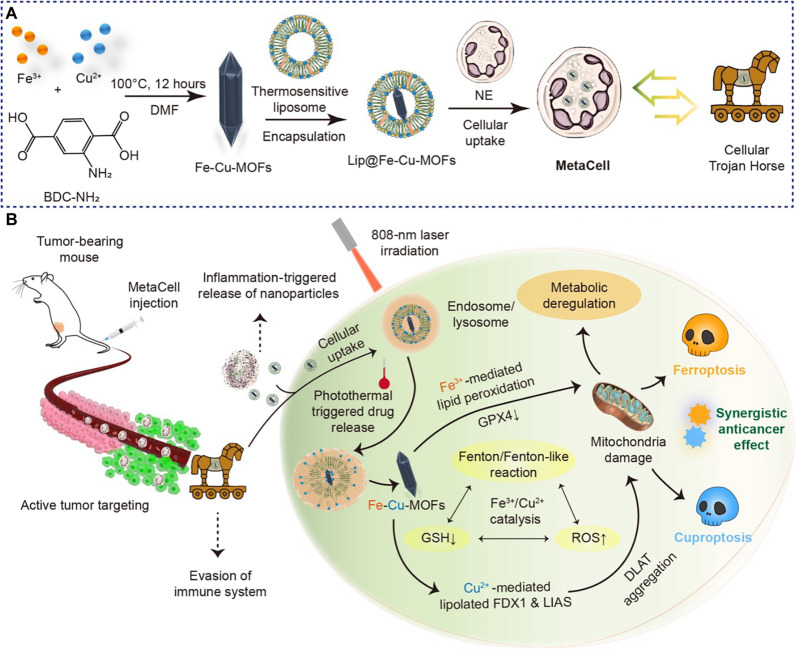
Fig. 1. An innovative cellular Trojan Horse strategy uses synergistic cuproptosis and ferroptosis for targeted cancer intervention.
(A) Design and preparation of cellular Trojan Horse (MetaCell). MetaCell comprises live neutrophils encapsulating a thermosensitive liposomal formulation of bimetallic Lip@Fe-Cu-MOFs. This innovative construct is created through an integrated fabrication strategy where Fe-Cu-MOFs are first synthesized by coordinating iron and copper metal ions with organic ligands, forming a well-defined porous framework. The Fe-Cu-MOFs are then incorporated within thermosensitive liposomes and subsequently internalized by live neutrophil (NE). This biomimetic approach endows MetaCell with a range of inherent neutrophil properties, resulting in a plethora of advantages. (B) A schematic illustration depicting the synergistic anticancer effects of cuproptosis and ferroptosis triggered by MetaCell. Taking advantage of the unique properties of neutrophils, MetaCell is designed to effectively evade the immune system. It not only infiltrates tumors but also responds to inflammation, releasing therapeutic components. This unique feature enables MetaCell to overcome traditional treatment barriers, notably enhancing its cancer treatment potential. In addition, MetaCell is programmed to respond to inflammation, instigating the release of Lip@Fe-Cu-MOFs within tumor. Once internalized, these thermosensitive liposomes discharge Fe-Cu-MOFs when exposed to NIR light, capitalizing on their potent photothermal properties. Moreover, photothermal heating not only stimulates the release of Fe-Cu-MOFs within cancer cells but also amplifies the simultaneous activation of cuproptosis and ferroptosis mediated by Fe-Cu-MOFs. By orchestrating this synergistic cell death, MetaCell targets diverse aspects of cancer biology, thereby enhancing therapeutic potency and substantially reducing the likelihood of cancer recurrence.