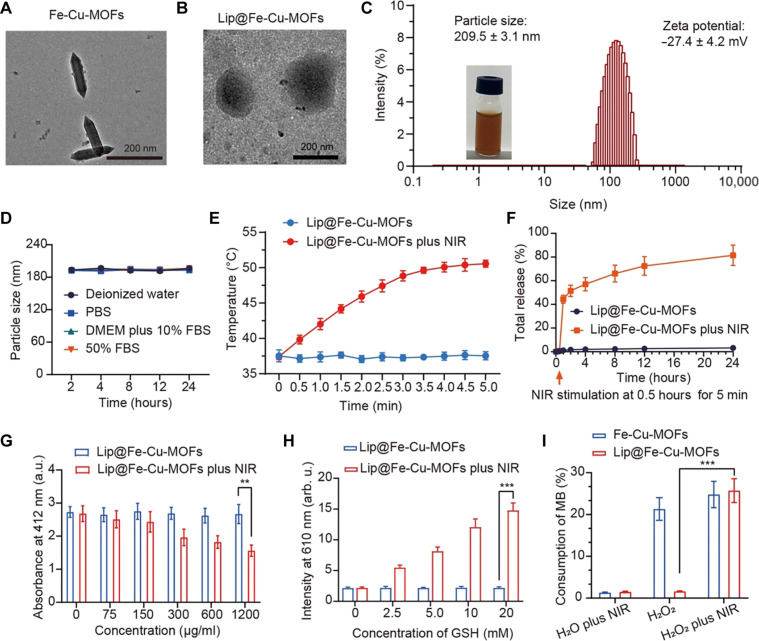
Fig. 2. Synthesis and characterization of Lip@Fe-Cu-MOFs.
(A) TEM images of Fe-Cu-MOFs. Scale bar, 200 nm. (B) TEM images of Lip@Fe-Cu-MOFs. Scale bar, 200 nm. (C) The size distribution and zeta potential of Lip@Fe-Cu-MOFs, measured by DLS. (D) Dynamic stability of Lip@Fe-Cu-MOFs. Measurement was tested in deionized water, phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), and 50% FBS, which was kept at 37°C for 48 hours. (E) Photothermal effects of Lip@Fe-Cu-MOFs. The temperature increasing profiles of Lip@Fe-Cu-MOFs was measured under NIR laser stimulation (808 nm, 1.5 W/cm2) for 5 min. (F) The time-dependent release of C6-labeled Fe-Cu-MOFs from Lip@Fe-Cu-MOFsC6 under specific conditions. The experimental setup assessed the release kinetics with and without the application of NIR stimulation (808 nm, 1.5 W/cm2) over a period of 5 min. The quantitative data reflecting the C6-labeled Fe-Cu-MOFs release was systematically recorded. (G) Lip@Fe-Cu-MOF–mediated GSH depletion, measured by the 5,5′-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB) assay. (H) Evaluation of Cu+ Generation. Lip@Fe-Cu-MOFs were incubated with various concentrations of GSH. Subsequently, the fluorescence intensity at a wavelength of 610 nm was measured, using an excitation wavelength of 365 nm. (I) Assessment of Lip@Fe-Cu-MOF–catalyzed Fenton-like reaction. The methylene blue (MB) assay was used to examine the catalytic capability of Lip@Fe-Cu-MOFs in promoting the Fenton-like reaction. This was conducted under NIR stimulation at 808 nm, with an intensity of 1.5 W/cm2 for a duration of 5 min. Data are presented as mean ± SD, with n = 3. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 (Student’s t test, two tails). a.u., absorbance units; arb. u., arbitrary units.