FIGURE 7.
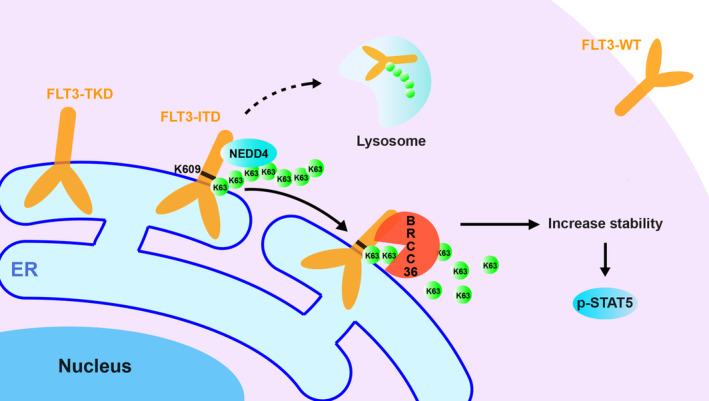
Schematic diagram of the proposed molecular mechanism for the specific interaction between FLT3‐ITD and BRCC36 for regulating cell functions. FLT3 is one of the most frequently mutated genes in AML, such as ITD and TKD, which shift the localization on the cell surface to ER, where both activate STAT5. Most patients harboring ITD mutants suffer from a worse relapse and poor survival rates. This study demonstrates that BRCC36, a K63‐linked polyubiquitin chain deubiquitinase, was selectively associated with ITD, not WT or TKD, enhancing its stability and downstream signaling, including p‐STAT5. Furthermore, we identified that K609, which links with the duplicate sequence in ITD, is a critical site for K63‐linked polyubiquitin, which is presumably modified by neural precursor cell‐expressed developmentally downregulated protein 4. 44 Thus, BRCC36 may be a promising target for novel therapy against FLT3‐ITD‐positive AML. The dotted line indicates the degradation pathway has not been directly proved in this study, necessitating further investigation.
