FIGURE 4.
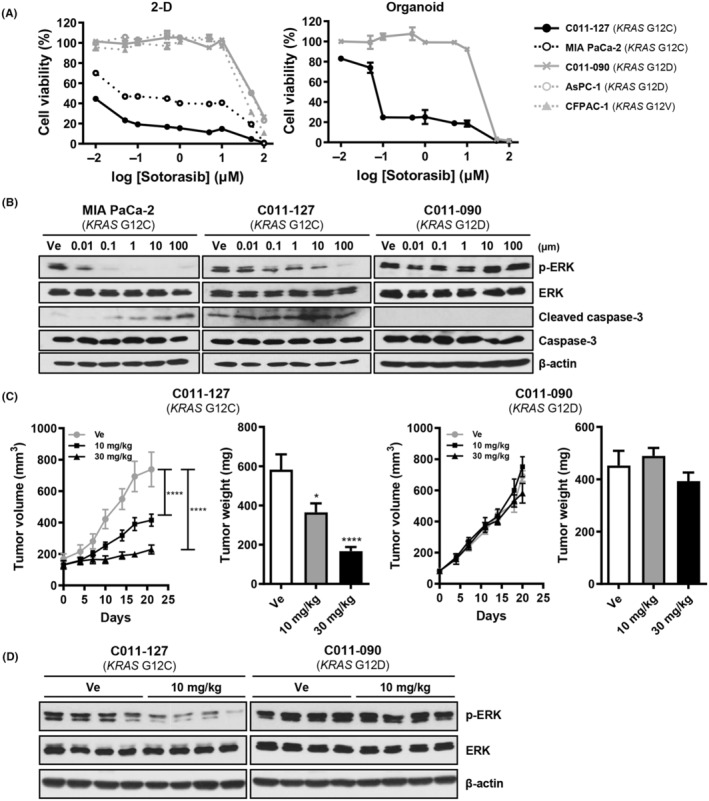
The KRAS G12C inhibitor sotorasib selectively inhibits tumor growth in a patient‐derived xenograft (PDX), PDX‐derived cell (PDXC), and PDX‐derived organoid (PDXO) with KRAS G12C mutation. (A) Drug response curve of sotorasib in 2D culture condition and organoid culture condition with 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, and 100 μM of sotorasib and vehicle (1% DMSO). The cell viability in 2D was observed after treatment for 72 h and measured using adenosine triphosphate (ATP)‐based assay with CellTiter‐Glo reagent. For the organoids, the ATP was measured after 5 days of treatment. (B) Western blot analysis for KRAS pathway (p‐ERK, ERK) and apoptosis (cleaved caspase‐3) on sotorasib‐treated MIA PaCa‐2, C011‐127‐PDXC (C011‐127‐PDX‐derived cell with KRAS G12C mutation), and C011‐090‐PDXC (C011‐090‐PDX‐derived cell with KRAS G12D mutation) for 24 h. (C) Tumor growth after administration of sotorasib. For the pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) xenograft mouse model, PDXC was injected into the flanks of BALB/c nude mice aged 5 weeks. Sotorasib was administered daily by oral gavage for 24 days starting at the time of tumor size of approximately 100–150 mm3. The tumor volume was measured twice a week. Tumor weights were measured immediately after euthanasia. (D) Western blot analysis for ERK phosphorylation in C011‐127‐PDX or C011‐090‐PDX tumor tissue after 24 days of administration.
