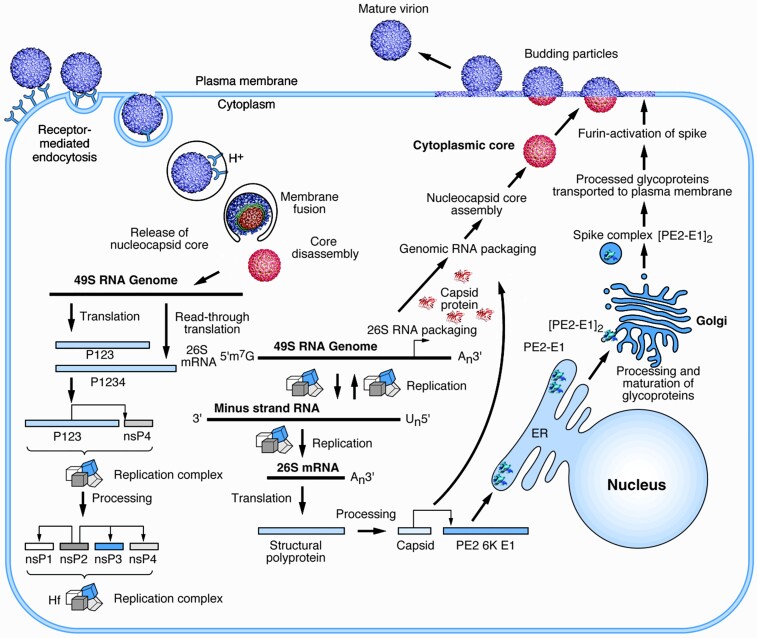
Figure 1.
Replication cycle of an alphavirus. The start of the cycle is shown on the left with the attachment of a virion to a cellular receptor. After fusion of the viral envelope, disassembly of the core, and release of the genomic ribonucleic acid (RNA), replication proteins are translated and processed (bottom left). These proteins enable the replication of the input genomic RNA (bottom center) and translation of the subgenomic messenger RNA (mRNA) into structural proteins. Cytoplasmic assembly of genomic RNA and capsid proteins produces the nucleocapsid core that associates with processed envelope glycoproteins (right) at the plasma membrane resulting in budding of infectious virions. Scale varies. Courtesy of Richard Kuhn with permission from the publisher [9]. ER, endoplasmic reticulum.