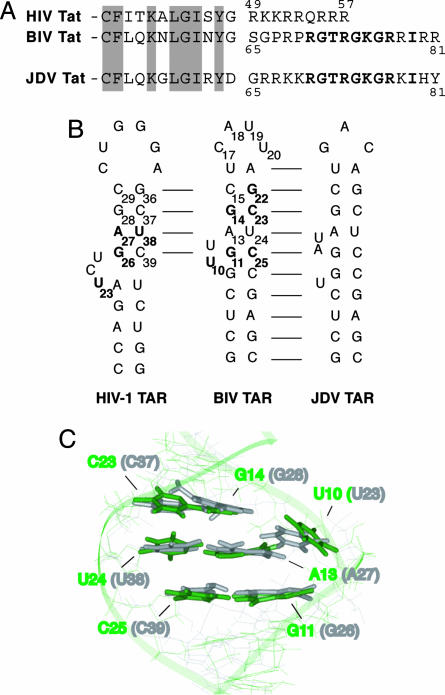
Fig. 1.
Comparison of Tat ARM domains and TAR RNAs. (A) The HIV-1, BIV, and JDV Tat ARM domains are aligned based on homology between the N-terminal activation domains (partially shown, with conserved residues shaded). Analogous residues in the BIV and the JDV Tat ARM are shown in bold. (B) Secondary structures of the HIV-1, BIV, and JDV TAR hairpins. Sequence identity is indicated by the lines, and nucleotides in HIV-1 and BIV TARs important for binding by the cognate protein are shown in bold. (C) Superimposition of the Tat binding sites in BIV TAR (green) and HIV-1 TAR (gray) in their bound conformations, from NMR models of the HIV-1 TAR-arginamide (19) and BIV Tat–TAR (28) complexes. The structures were superimposed by using all bases known to be important for binding of each, and the corresponding base numbering is shown for both RNAs.