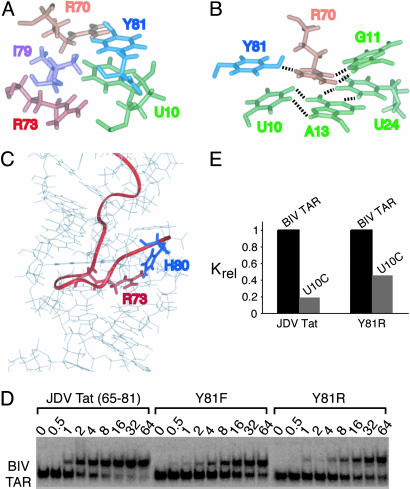
Fig. 4.
Interactions involving the C-terminal end of the JDV Tat ARM and effects of mutations on binding affinity. (A) View of the average minimized structure showing the stacking interaction between Tyr-81 and the U10 residue and the surrounding hydrophobic pocket delineated by the side chains of Arg-70, Arg-73, and Ile-79. (B) View showing the likely hydrogen bonding interactions of the Arg-70 (orange) guanidinium group with the Tyr-81 (blue) hydroxyl group and the Hoogsteen face of G11 located above the base triple (green). Groups within hydrogen bonding distance are indicated by dashed lines. (C) View of one representative structure showing the positions of His-80 and Arg-73 within hydrogen-bonding distance. The positions of the Arg-70, Arg-73, and His-80 side chains are well defined in the ensemble of structures despite the absence of electrostatic constraints imposed on the calculations. (D) Binding of the JDV Tat peptide and mutants to BIV TAR using gel mobility-shift assays. Binding reactions were performed at the peptide concentrations indicated with 0.2 nM RNA, and dissociation constants were calculated as described in Materials and Methods.(E) Binding of the JDV Tat peptide and Y81R mutant to BIV TAR and U10C mutant RNAs. For each peptide, relative association constants, as determined in D, were normalized to the values obtained with BIV TAR.