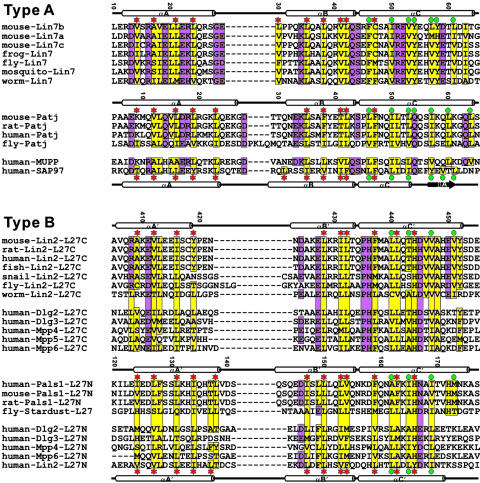
Fig. 2.
Amino acid sequence alignment of selected L27 domains derived from the 3D structures of three different complexes. In this alignment, the secondary structures of L27 domains with known 3D structures are shown at the top of each sequence. The highly conserved hydrophobic residues are highlighted in yellow. The other conserved residues are shown in purple. The amino acid residues involved in the L27SAP97/L27Lin2N heterodimer packing are indicated with red asterisks, and the amino acid residues involved in the packing of the central four-helix bundle of the tetramer are highlighted with turquoise dots. One may note from this structure-based sequence alignment that the structural role of the αC-helix in the type A and type B L27 domains (see ref. 17 for domain classification) is significantly different. In the type A L27 domains, the αC-helix is primarily involved in the packing of the central four-helix bundle. With the exception of one residue in the N terminus of the helix, the rest of the helix makes very little contact with the αA- and αB-helices. In contrast, in addition to an involvement in the formation of the central four-helix bundle, the αC-helix in each type B L27 domain also packs intimately with the αA- and αB-helices from the same domain.