Figure 3.
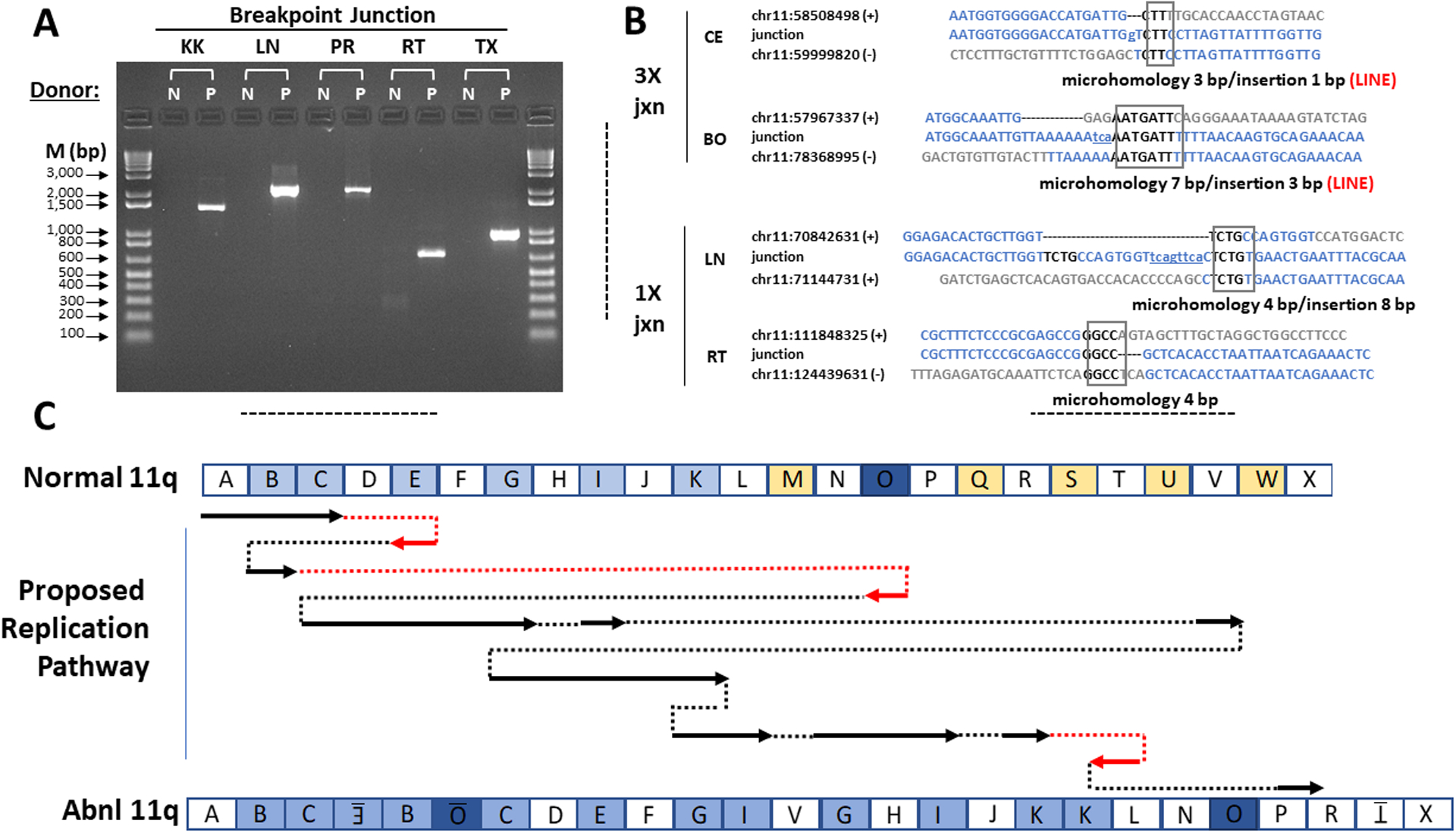
Microhomology-Mediated Break-Induced Replication as a potential mechanism for chromoanasynthesis. (A) Confirmation of patient chromosome 11 breakpoint junctions by PCR. Donors: N, normal control; P, patient. PCR primers were designed to amplify DNA only from the breakpoint junctions identified from patient DNA by whole genome sequencing. The names of the breakpoint junctions are composed of the two flanking segment names as defined in Figures 2C and 3C. M, markers (base pairs). (B) Breakpoint junction sequence analysis. Four of the 12 breakpoint junction sequences determined by the Sanger method are shown. The other junction sequences are in Figure S4B. At left is indicated the type of copy number variation at the indicated junction. The name of each junction is formed by the adjacent segments as defined in Figures 2C and 3C. For each junction, the top and bottom sequences shown in blue are those of the reference sequence + and - strands that contribute to the junction. The number is the chromosome 11 position from the hg19 reference sequence of the first nucleotide shown. The middle sequences are those determined experimentally by the Sanger method for the patient using primers designed to flank each breakpoint junction. The boxed sequence denotes regions of microhomology in the junction, and the lower-case and underlined nucleotides denote insertions, as summarized below each alignment. Both 3X junctions occurred at a LINE sequence as indicated by the word LINE in red. The BE breakpoint could not be validated with Sanger sequencing due to surrounding inverted LINE sequences. (C) Proposed chromoanasynthesis replication pathway on chromosome 11q in Jacobsen Syndrome patient. The top and bottom models of chromosome 11q are segmented according to the experimentally determined breakpoints as defined in Figure 2. In the proposed replication pathway, arrows denote regions of normal chromosome 11q that appear in the derivative patient chromosome 11q, either in the normal orientation (black) or inverted (red). Dotted lines indicate movement from one replication fork to another, either in the normal orientation (black) or the opposite orientation (red).
