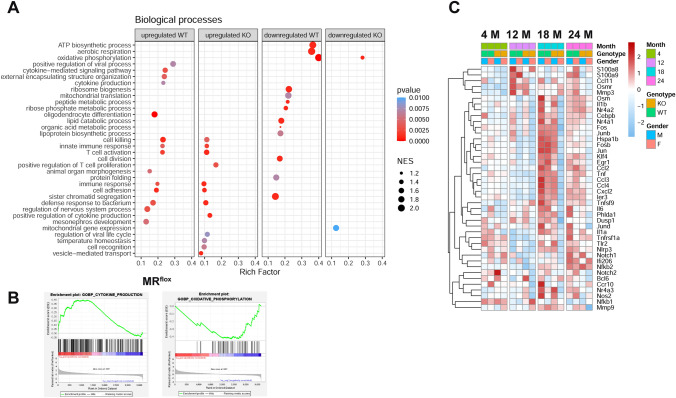
Fig. 1.
MR deficiency protects against macrophage inflammaging. Cardiac macrophages, identified as CD45+/CD11b+/CD64+ and MERTK+, were FACS sorted from hearts of male/female young (4 months-old), middle-aged (12 months-old), and old (18 and 24 months-old) MRflox and MRLysMCre mice. A Comparison of biological processes significantly altered (p < 0.01) over time in macrophages between MRflox (WT) and MRLysMCre (KO) mice determined by gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA). Parent terms following redundant Gene Ontology terms reduction are shown, except for some child terms when the relative parent terms did not appear in both genotypes. Rich factor is the ratio of differentially expressed gene number (Size) annotated in a pathway term to all gene number annotated. Greater rich factor means greater intensiveness. NES: normalized enrichment score determined by GSEA. B GSEA plots of upregulated cytokine production and downregulated oxidative phosphorylation pathways in macrophages from MRflox mice. C Heatmap showing z score normalized expression values of selected genes over the course of aging in the range 4 to 24 months related to inflammatory macrophages from MRflox (WT) and MRLysMCre (KO) mice reported on published single-cells RNA-seq data or belonging to leading edges of GSEA