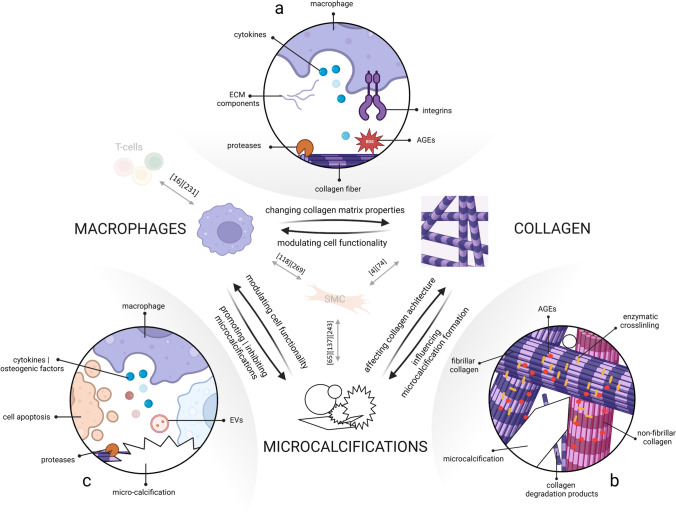
Fig. 2.
The interplay between the main cap components: collagen, macrophages, and microcalcifications and essential reviews discussing the influence of SMC’s and T cells on these components [16, 65, 74, 118, 137, 231, 243, 269]. A Macrophages influence the collagenous matrix by secretion of cytokines, ECM components, AGEs, and proteases. Furthermore, integrins detect matrix properties and regulate processes of macrophage biology, by which the collagenous matrix properties, thus, modulate cell functionality. B Collagen serves as a scaffold for microcalcification formation and collagen type, cross-linking and degradation can affect the formation of microcalcifications. Furthermore, microcalcifications themselves affect collagen architecture. C Macrophages release cytokines, osteogenic factors, proteases, and EVs that can alter calcification formation. In addition, macrophage apoptosis contributes to microcalcification formation. Microcalcifications, in turn, modulate macrophage functionality by promoting release of pro- or anti-inflammatory factors.
Created with BioRender.com