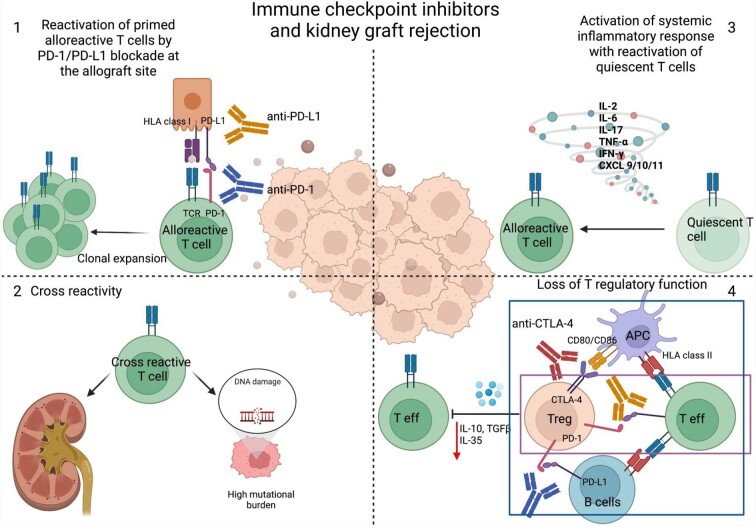
Figure 2:
Potential mechanisms involved in kidney allograft rejection in the context of ICI. (1) Reactivation of alloreactive quiescent T cells by blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway. (2) Cross-reactivity between tumoral neoantigens and kidney allograft antigens. (3) Systemic inflammation can cause overactivation of the immune system, with off-target effects and potential activation of dormant alloreactive T cells. (4) CTLA-4 expressed on Tregs interacts with co-stimulatory molecules CD80/86 preventing APCs from effectively stimulating effector T cells. CTLA-4 can also directly interact with CD80/86 expressed on effector T cells. PD-1 on Treg prevents alloreactive B cells from stimulating other T cells and can inhibit directly T effector cells expressing PD-L1. Blocking both pathways leads to loss of regulatory T cells function and activation of host alloimmune responses.