Fig. 4 |. Structure-based discovery of a chemical AE1 inhibitors.
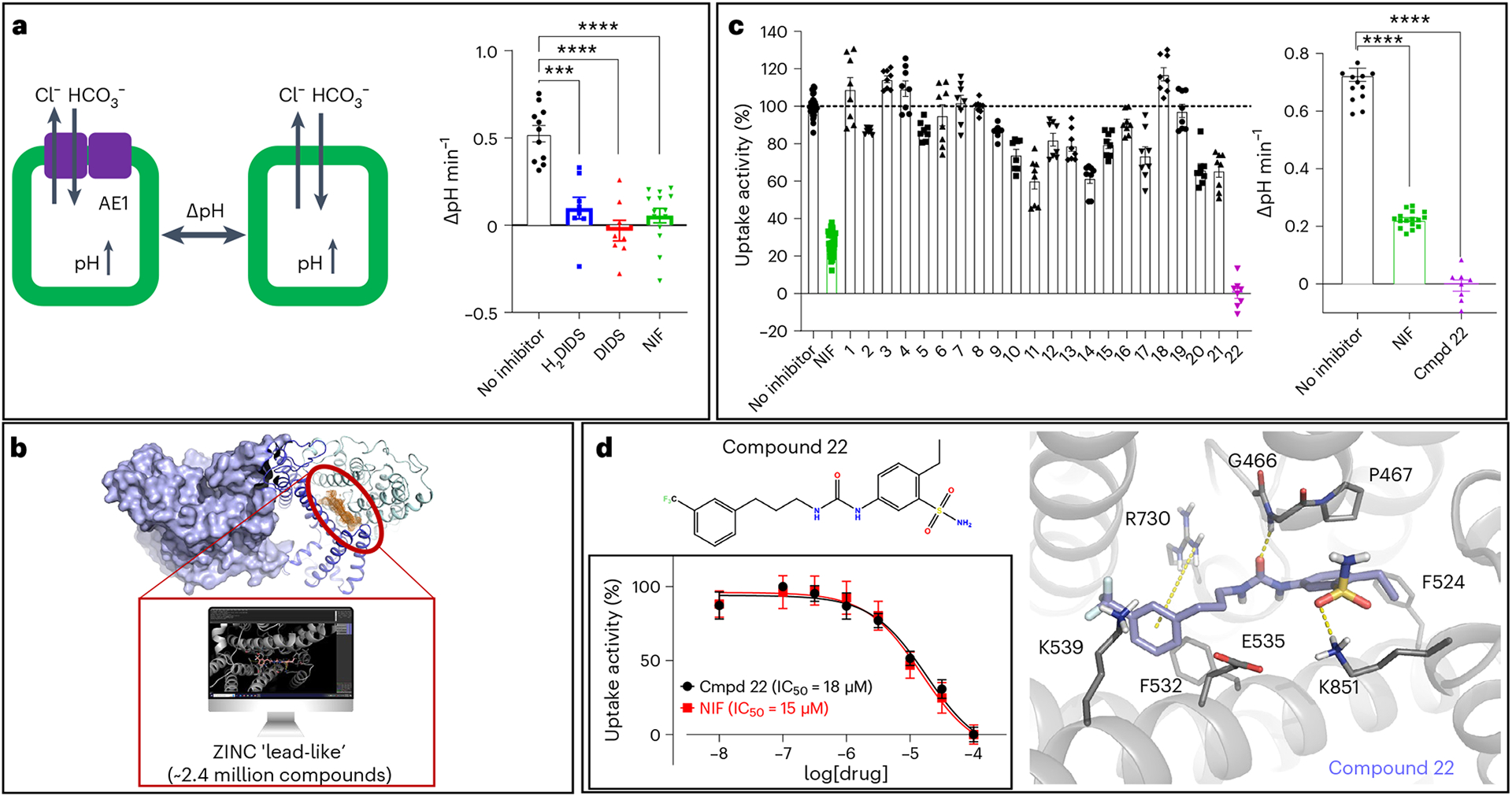
a, Measurement of cellular bicarbonate uptake in an inducible Flp-In T-REx 293 cell line, via cellular pH increase in response to AE1-mediated bicarbonate transport. AE1-specific activity was determined as pH differences measured after 1 min of uptake between uninduced and induced cells. H2DIDS (20 μM followed by washout), DIDS (20 μM followed by washout) and NIF (50 μM) show statistically significant AE1 inhibition. Uptake experiments were performed with 2–6 technical repeats and are averaged from three independent experiments (n = 3). Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. Statistical significance was determined via one-way ANOVA (Dunnett’s multiple comparison); ***P < 0.0001, ****P < 0.0001; P = 0.0002400 (H2DIDS), P = 0.0000070 (DIDS), P = 0.0000005 (NIF). b, 2.4 million purchasable compounds from the ZINC library were docked against the herein defined substrate binding site (orange mesh) of the apo and DIDS-bound AE1 structures. c, A total of 22 compounds were experimentally tested for inhibitory activity, and compound 22 shows inhibitory activity at 50 μM in a single dose experiment. Uptake experiments were performed with 2–6 technical repeats and are averaged from three independent experiments (n = 3). Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. Statistical significance was determined via one-way ANOVA (Dunnett’s multiple comparison); ****P < 10−14. d, Chemical structure and docking pose of compound 22 from virtual screening. Compound and transporter are shown in violet and gray, respectively, and hydrogen bonds, salt bridges and pi–cation interactions are indicated as yellow dashes. Concentration response experiments reveal comparable inhibitory potencies of compound 22 (IC50 = 18 μM, pIC50 = 4.746 ± 0.049) and NIF (IC50 = 15 μM, pIC50 = 4.823 ± 0.064). Apparent potencies are calculated as IC50 (mean) and pIC50 (mean ± s.e.m.). Uptake experiments were performed in triplicate and are averaged from four independent experiments (n = 4), and data are represented as mean ± s.e.m.
