Extended Data Fig. 1 |. Cryo-EM structure determination of AE1 complexes as exemplified by AE1-DIDS complex.
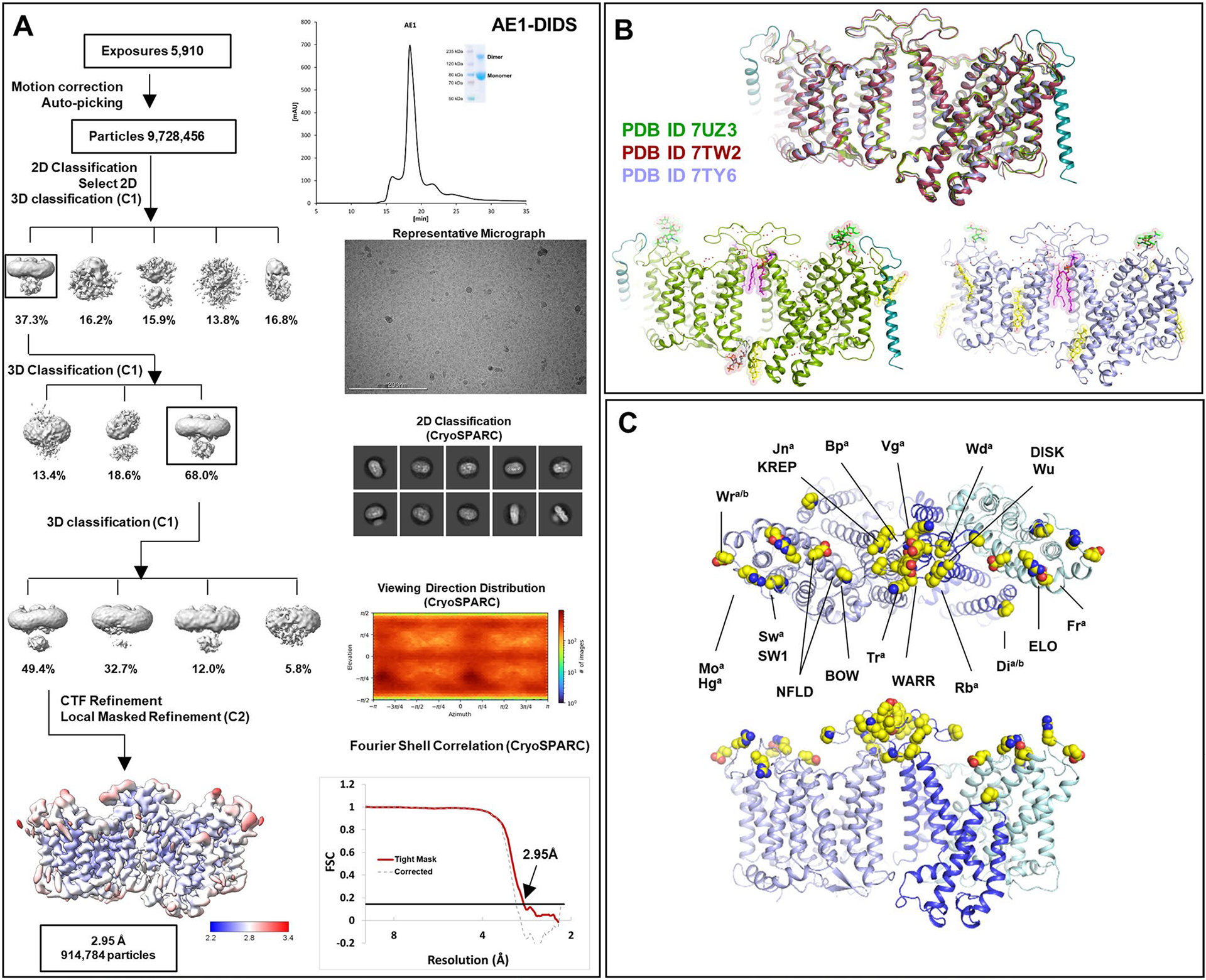
a, Analytical size exclusion chromatography and SDS-PAGE show monodisperse and pure protein of AE1-DIDS. Data were collected on 300 keV Krios, a representative micrograph is shown, and processed in cryoSPARC: particles were picked from motion corrected micrographs, subjected to 2D classification (representative classes are shown), followed by ab initio model building and 3D classification. After multiple rounds of 3D classification, the final particle stack was subjected to local CTF refinement followed by local refinement of the masked AE1 membrane domain with imposed C2 symmetry. Final map was obtained with GS-FSC indicating a resolution of 2.95 Å (AE1-DIDS) applying the 0.143 cutoff. Viewing direction distribution analysis (cryoSPARC) indicates sufficient coverage. An initial model was built in PHENIX, and then further refined in ServalCat for the generation of final maps and coordinates of mdAE1. Calculations in cryoSPARC indicate local resolutions of up to 2.5 Å around substrate and inhibitor binding sites. Viewing direction analysis indicates isotropic distribution of views in final particle stack. b, Superposition with other AE1 structures (AE1, PDB ID: 7TW2, dark red; AE1-Glycophorin complex, PDB ID: 7UZ3, lime green)7,8. Root mean square deviations of 0.997 Å (7TW2) and 0.372 Å (7UZ3) highlight similarity of protein conformation. Glycosylation modifications, cholesterols, lipids, waters, PIP2, and Glycophorin are shown in green, yellow, purple, red, grey, and teal, respectively. c, Cryo-EM structures allowed us to assign the complete extracellular surface including all Diego antigens (see Extended Data Table 2) with sidechains shown as spheres with yellow carbon atoms.
