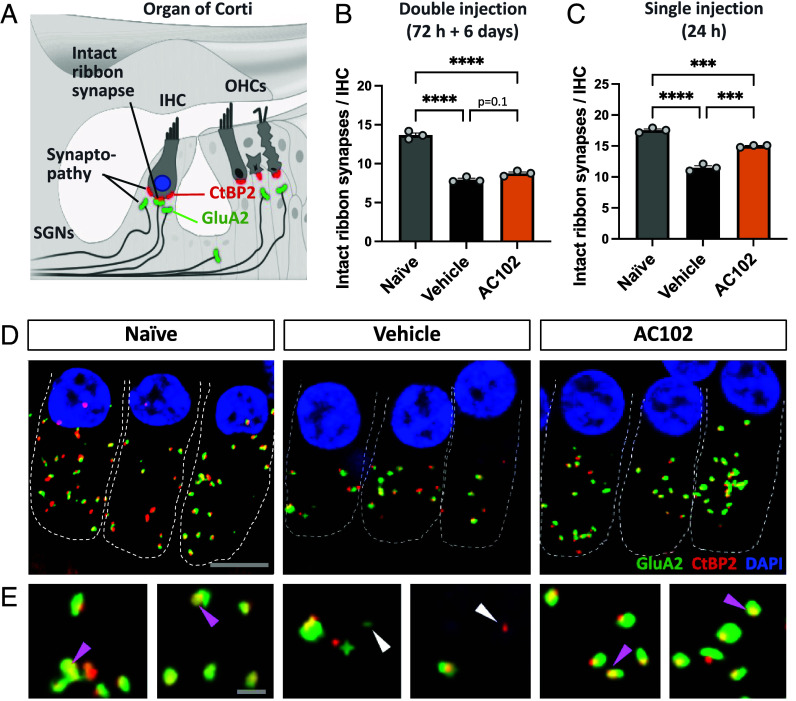
Fig. 3.
Effect of AC102 on synaptopathy after noise exposure in vivo. (A) Schematic overview of staining paradigm: pre- and postsynaptic proteins were stained by CtBP2 (red) and GluA2 (green), respectively. Colocalization labeled intact ribbon synapses, whereas individual staining labeled synaptopathy. SGNs = spiral ganglion neurites. (B) Quantification of pre- and postsynaptic pairs of CtBP2- and GluA2-labeled puncta 14 d after noise exposure at the 16 kHz region revealed that a delayed double injection of AC102 (72 h and 6 d after noise exposure; SI Appendix, Fig. S1) does not affect synaptopathy. (C) In contrast, a highly significant reduction of synaptopathy is observed when AC102 is locally applied as single injection (24 h after noise exposure; Fig. 1C). Data shown as mean ± SEM. n = 3 per group and experiment. ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001. (D) Representative confocal images of IHCs and their ribbon synapses in naïve, vehicle and AC102-treated animals from experiment shown in C. (Scale bar, 10 µm.) (E) High magnification images of ribbon synapses from D. Purple arrows denote paired, and white arrows denote unpaired receptor patches. (Scale bar, 2 µm.)