Figure 5.
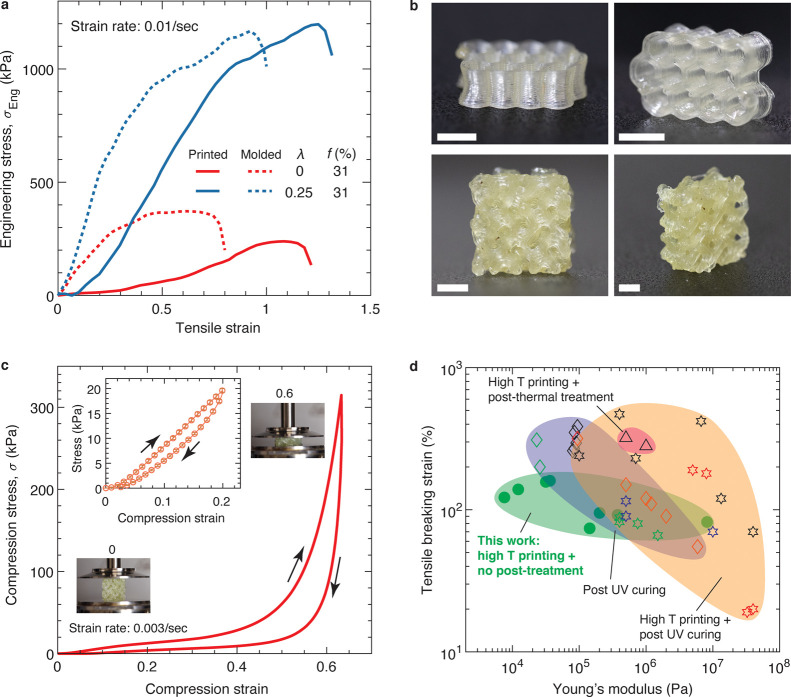
DIW printing of LAL polymers to produce highly deformable 3D structures. (a) Stress–strain behavior of 3D printed and molded tensile bars of LAL polymers tested at room temperature and 0.01/s strain rate. (b) Photos of honeycomb (upper) and gyroid (lower) structures printed using an LAL polymer (f = 31%, λ = 0.25%). The light yellowish color is attributed to reprocessing of the polymers at high temperatures and contamination by the extruder. Scale bars: 5 mm. (c) Compression stress–strain behavior of the 3D printed gyroid in (b). The compression strain rate is 0.003/s. Inset: cyclic compression–release profile exhibits a hysteresis for the deformation of 20%. Error bar: standard deviation for n = 4. (d) Ashby-type plot comparing elastomers for solvent-free DIW printing based on tensile breaking strain and Young’s modulus. Filled green circles: our modular soft elastomers; other symbols: literature data (Table S2).