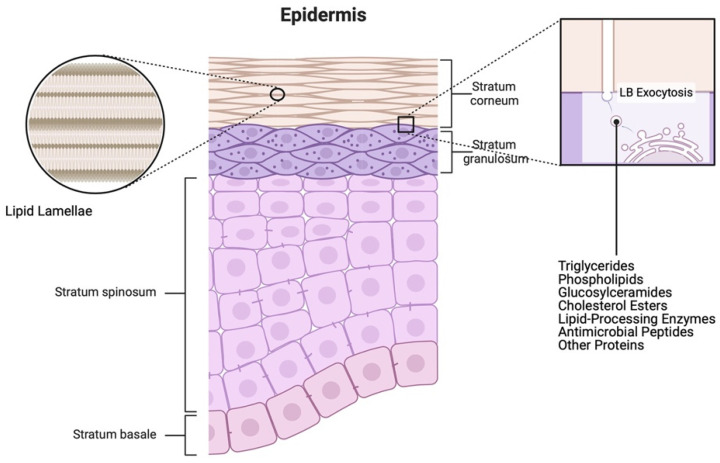
Figure 1.
Schematics illustrating the structure of the epidermis and the lamellar body/lipid secretion process. The epidermis primarily consists of keratinocytes arranged in layers. Proliferating keratinocytes reside in the stratum basale, followed by suprabasal keratinocytes in the stratum spinosum, lamellar body (LB)-secreting keratinocytes in the stratum granulosum, and terminally differentiated (dead) keratinocytes (squames or corneocytes) in the stratum corneum. The square inset on the right depicts the composition and exocytosis of LB by differentiating keratinocytes in the stratum granulosum. Lipids secreted via LBs contribute to the formation of lipid lamellae surrounding the corneocytes, establishing the skin’s lipid barrier, as illustrated in the left circular inset. Created with Biorender.com.