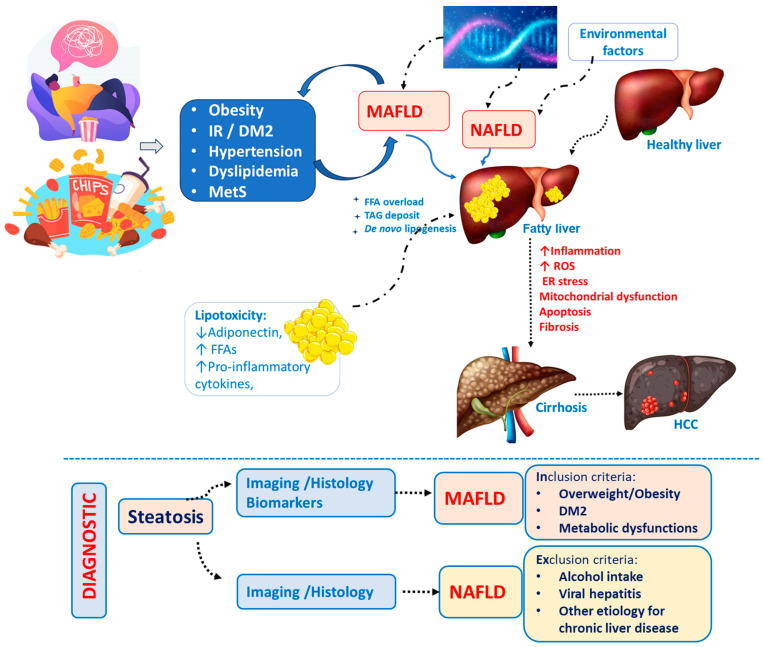
Figure 1.
Differences between the diagnosis and definition of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) stem from environmental factors and genetics, which contribute to increased lipid deposition in liver tissue, leading to inflammation and oxidative stress. In NAFLD, the presence of steatosis is primarily related to genetics but not to other causes beyond insulin resistance. DM2: type 2 diabetes mellitus; ER: endoplasmic reticulum; FFAs: free fatty acids; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; MetS: metabolic syndrome; ROS: reactive oxygen species; TAG: triglycerides.