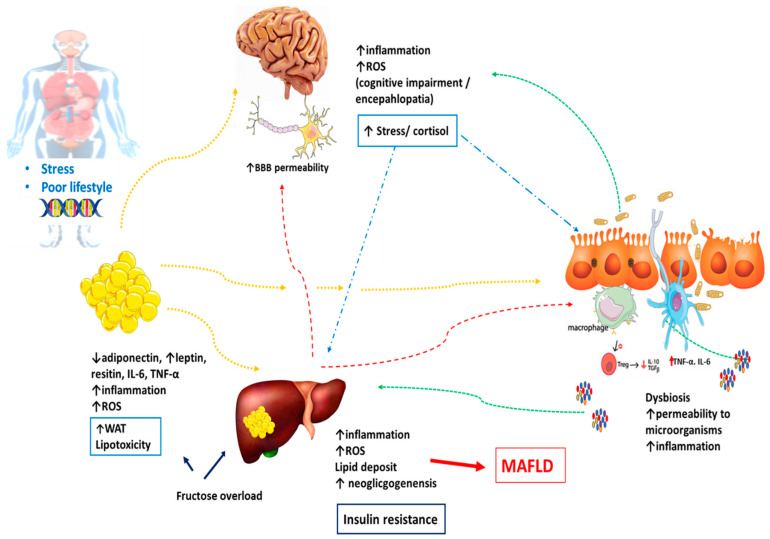
Figure 3.
The relationships of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). Increased gut permeability triggers immune system activation and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines that contribute to brain inflammation and the production of stressors, which is related to increased inflammation and oxidative stress in the liver. The products of the low-grade inflammation of adipose tissue aggravate this pro-inflammatory scenario, which contributes to systemic inflammation, leading to cognitive impairment. IL-6: Interleukin-6; ROS: reactive oxygen species; TNF-α: Tumor Necrosis Factor-α. The colored arrows only indicate the interrelationships between one organ/system and another.